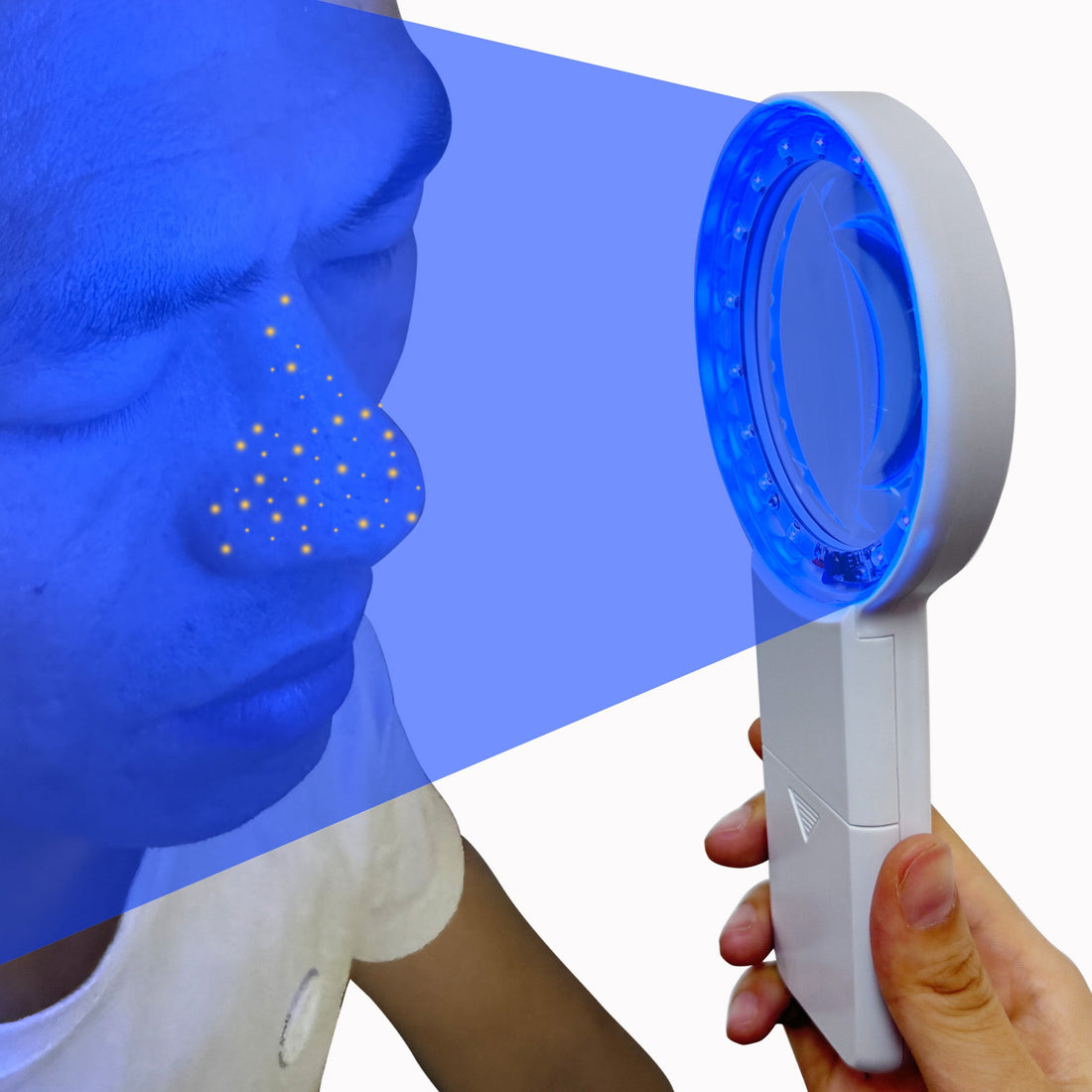
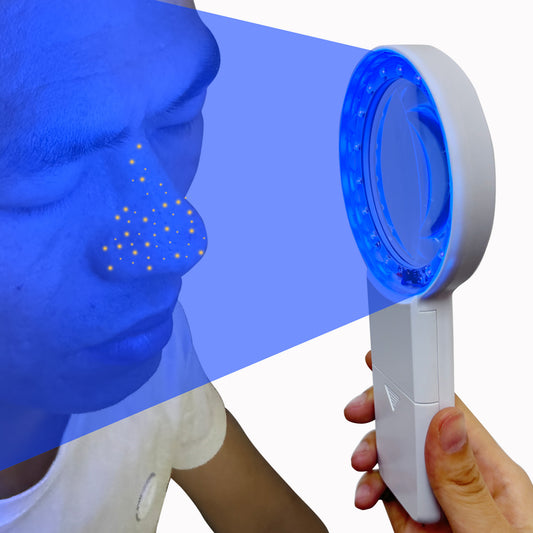
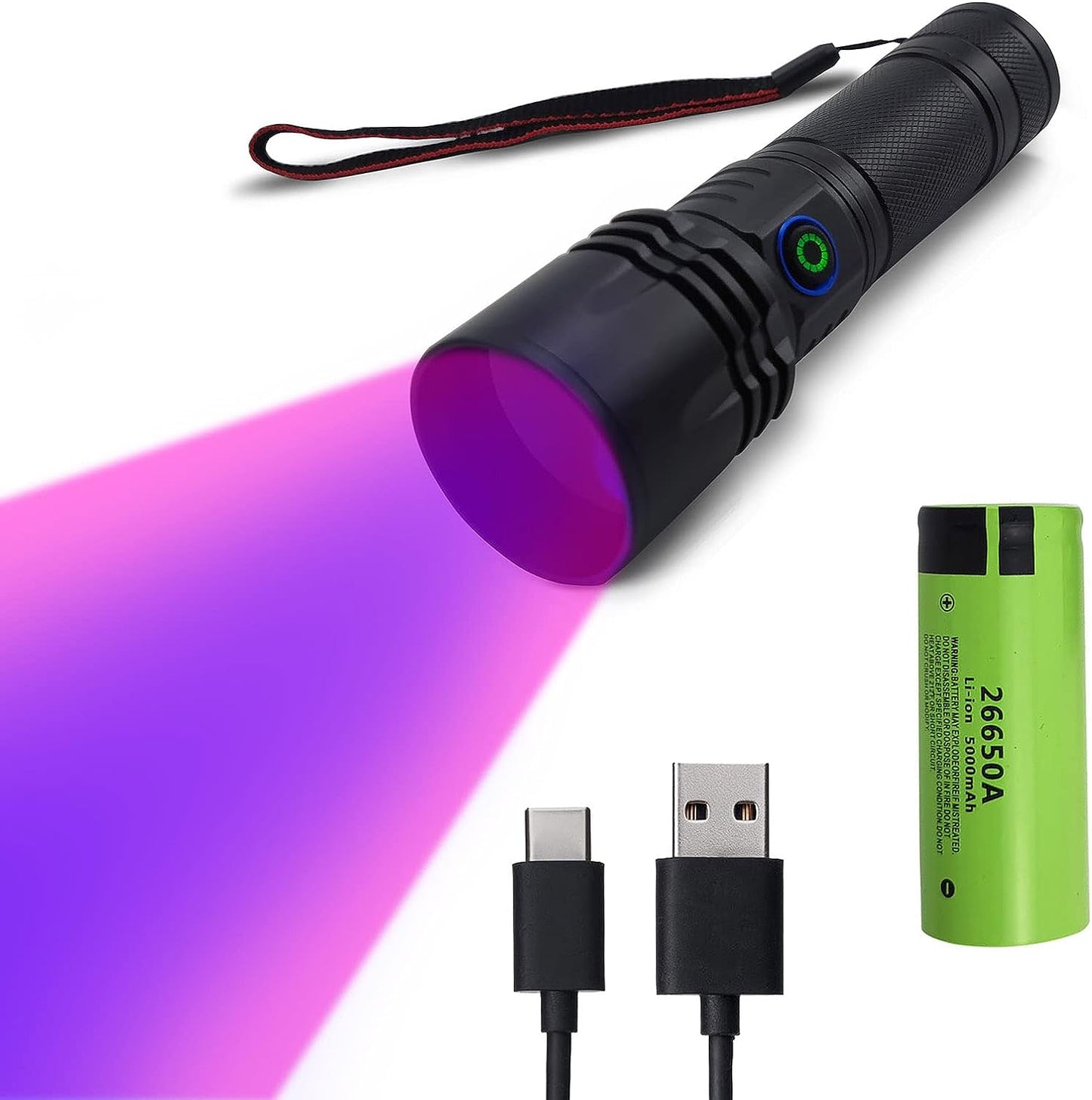
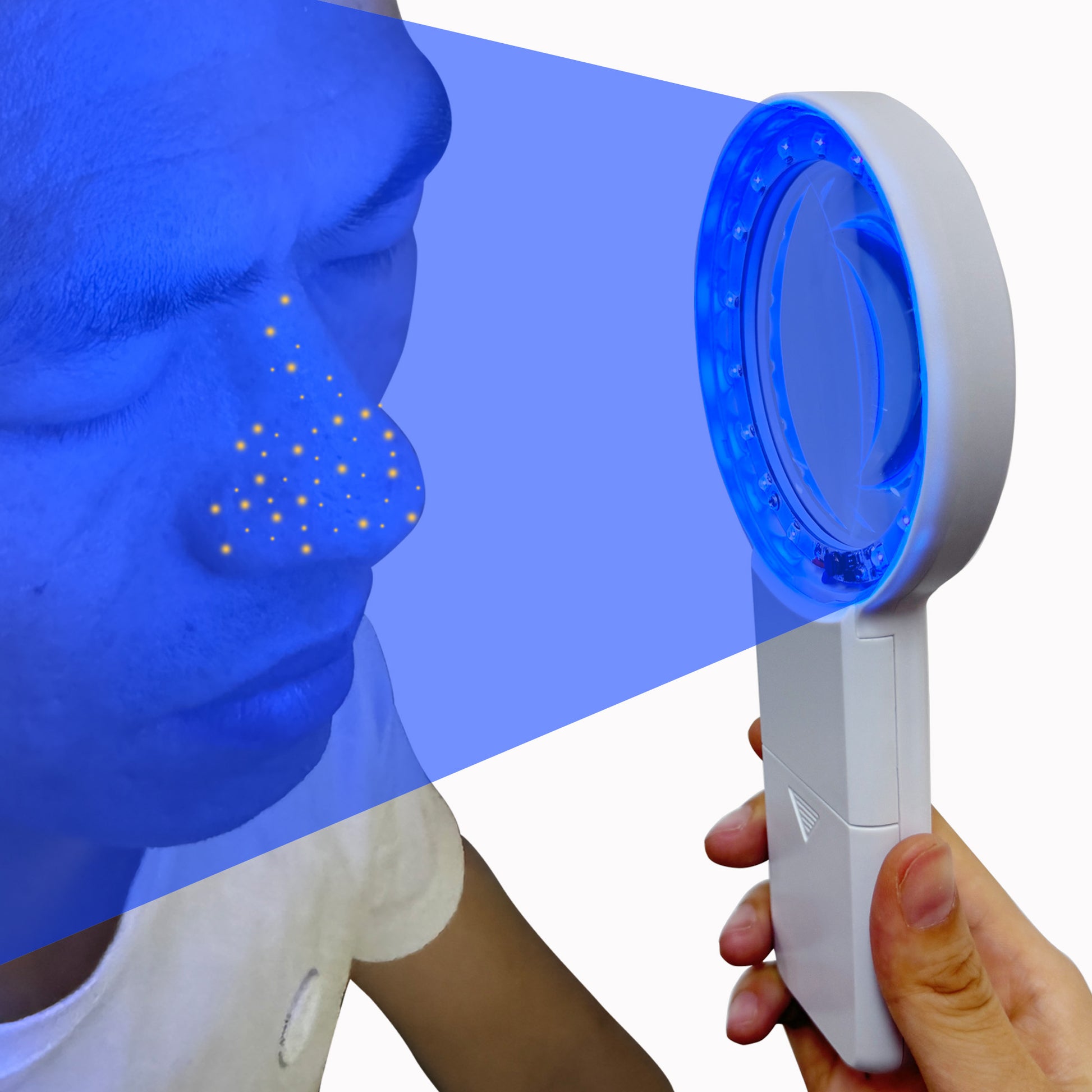
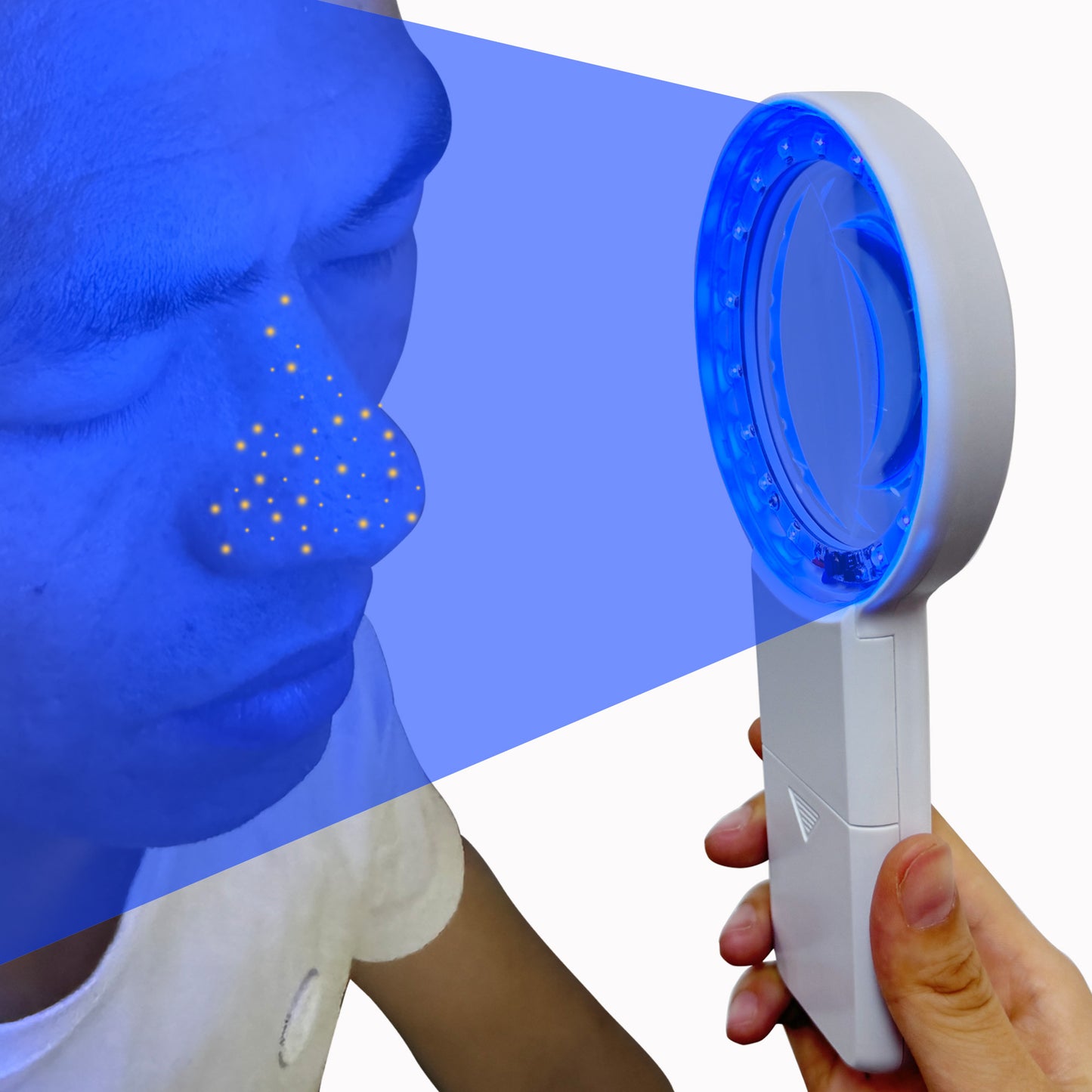
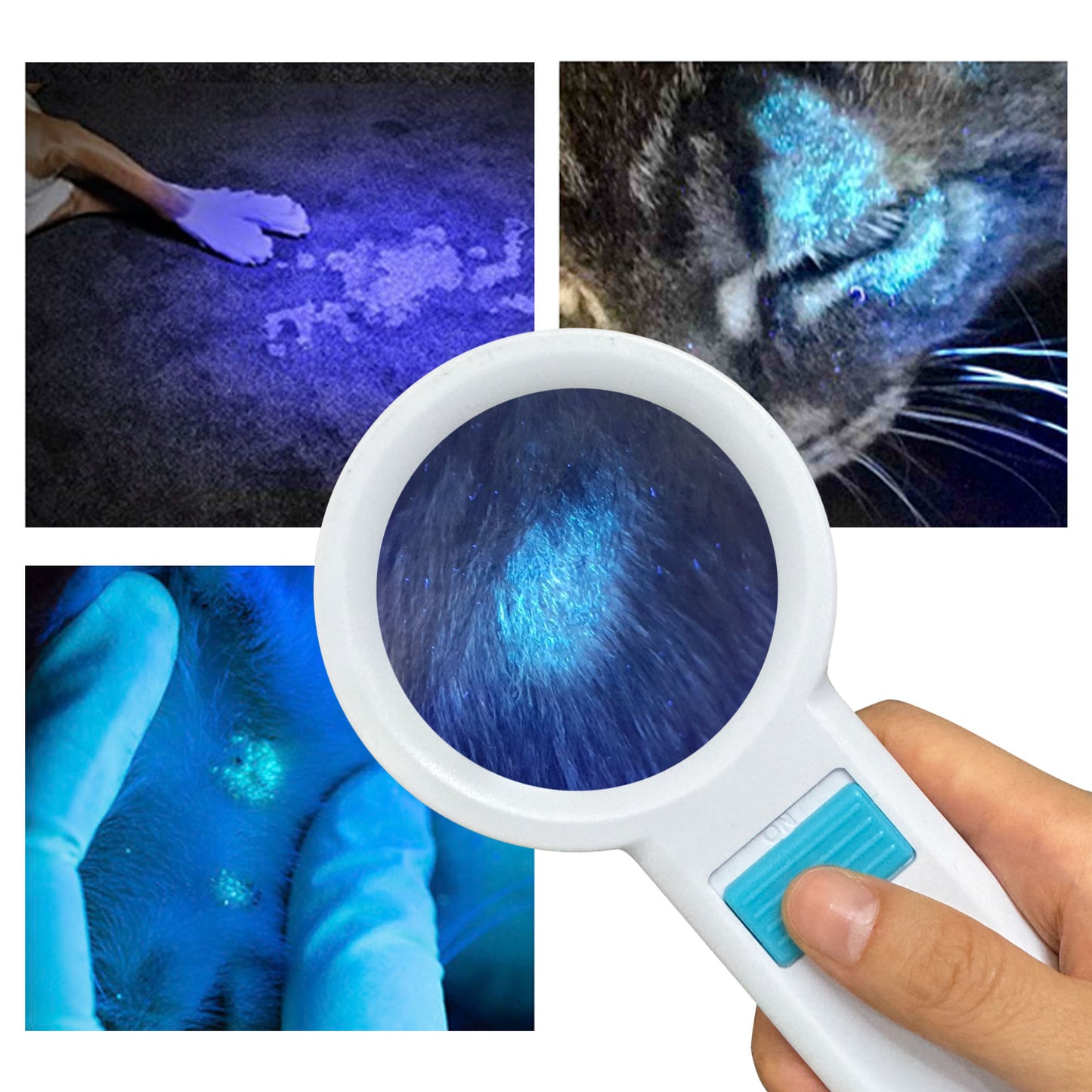
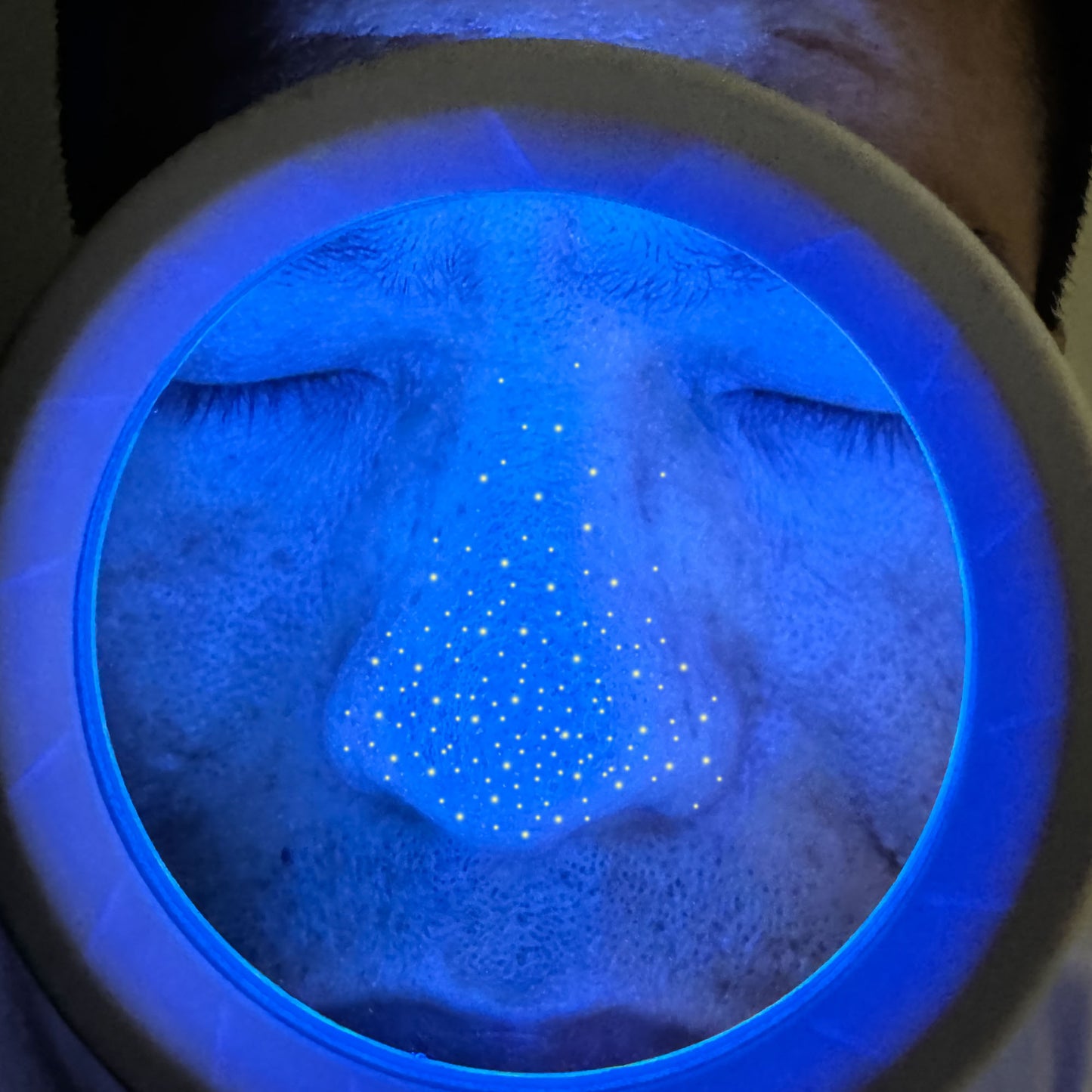
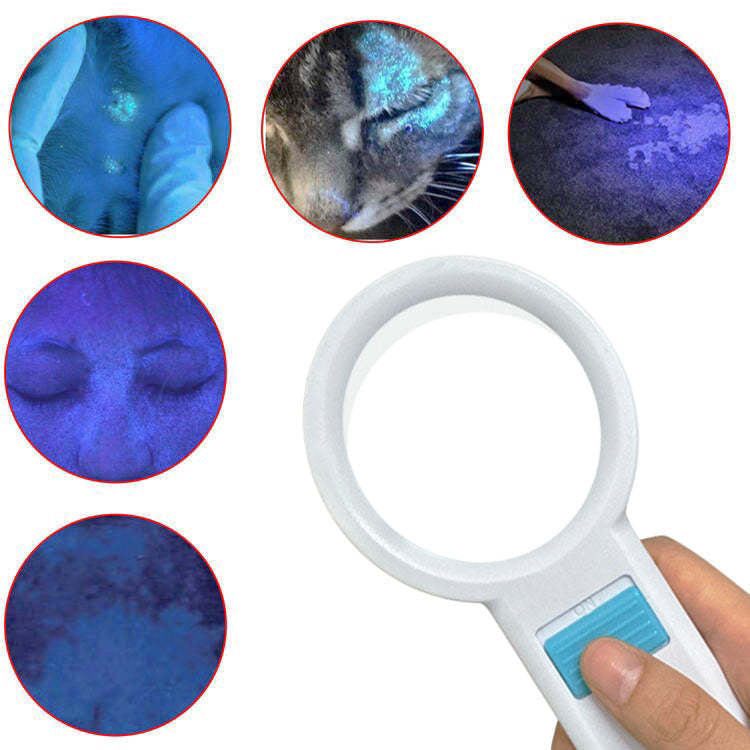
How does a Woods lamp work?
Video
Featured collection
-
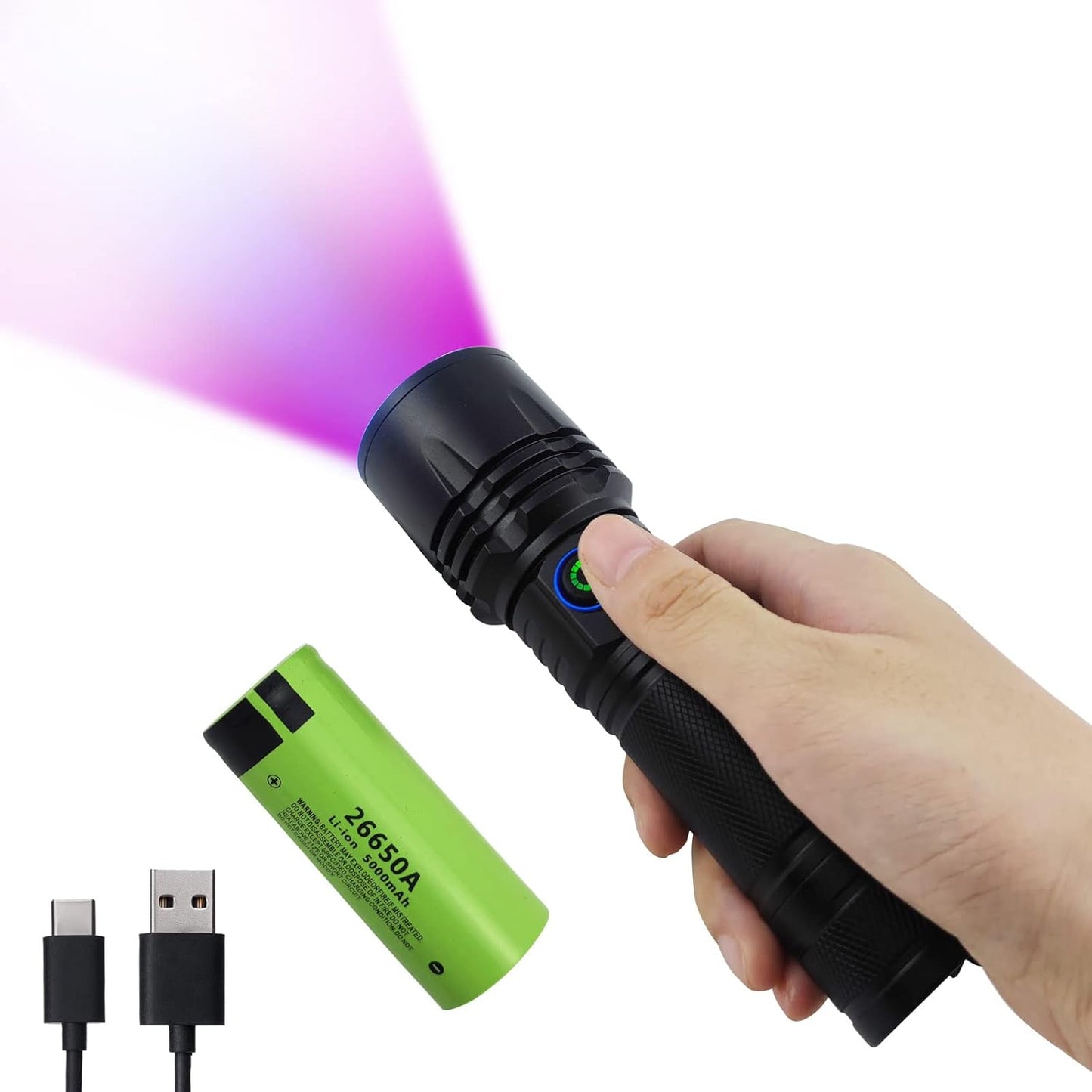
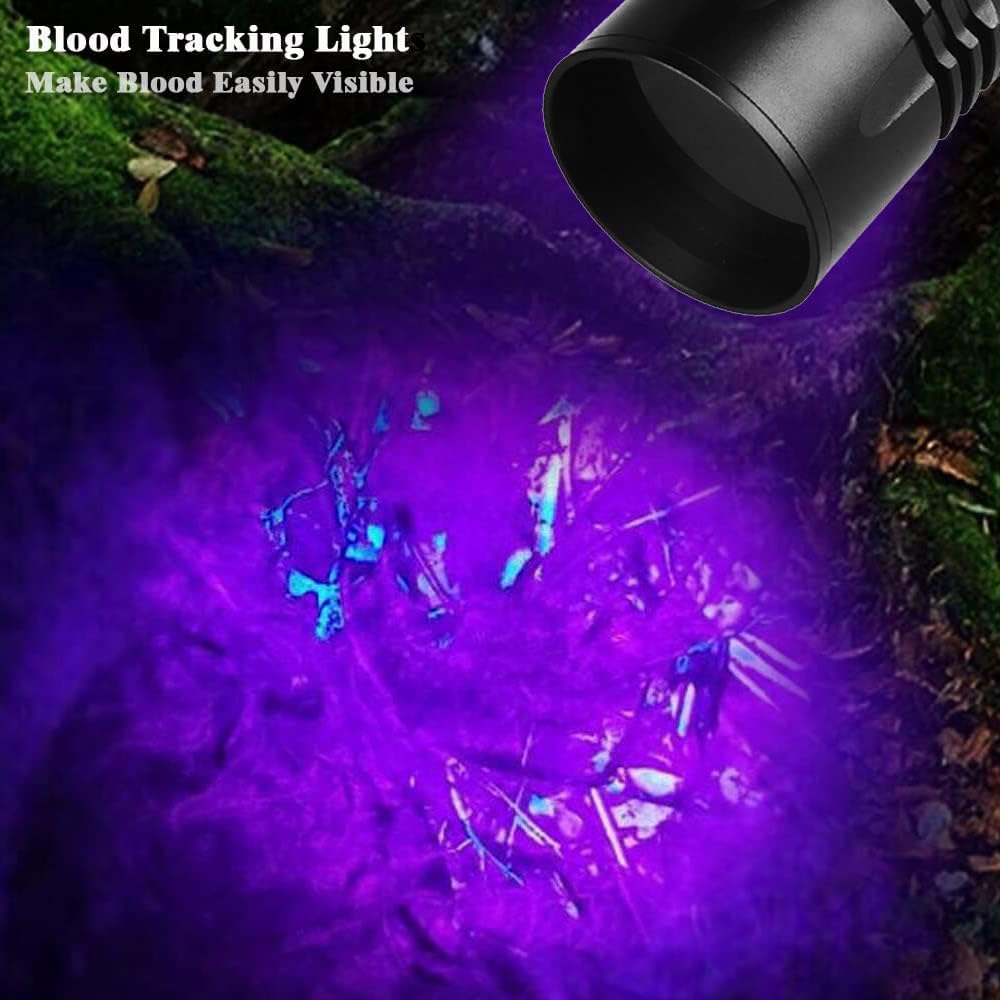
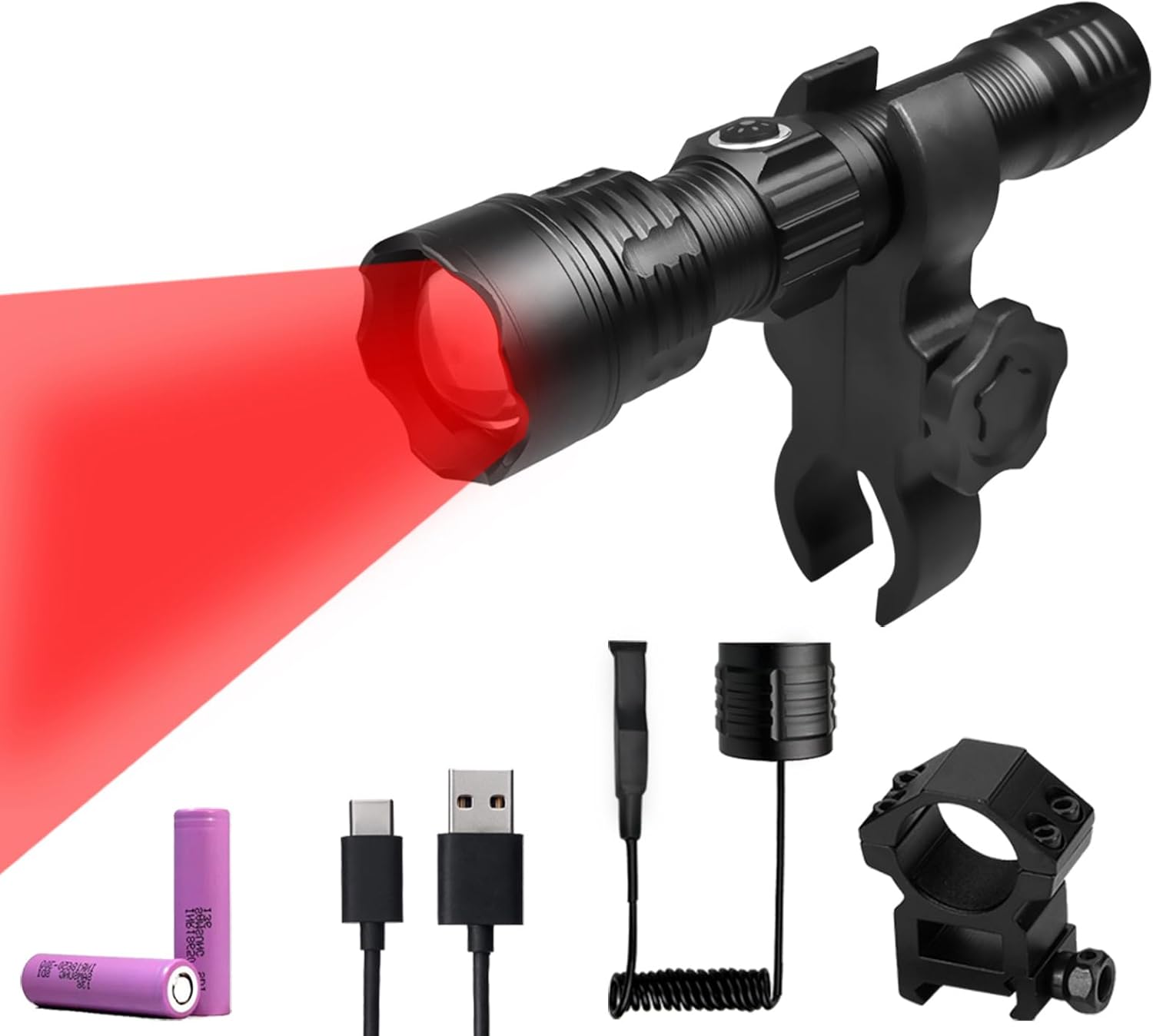
Uv Blood Tracking Flashlight for Hunting Deer Finder Blood Trailing Light Rechargeable Blood Tracker Light
通常価格 $29.99から通常価格単価 / あたり$79.99セール価格 $29.99からセール -
Rechargeable Blood Tracking Light for Night Hunting 2000 Lumens Blood Trail Tracking Flashlight Gifts for Hunter (Blood Finder Light)
通常価格 $39.99通常価格単価 / あたり$69.99セール価格 $39.99セール -
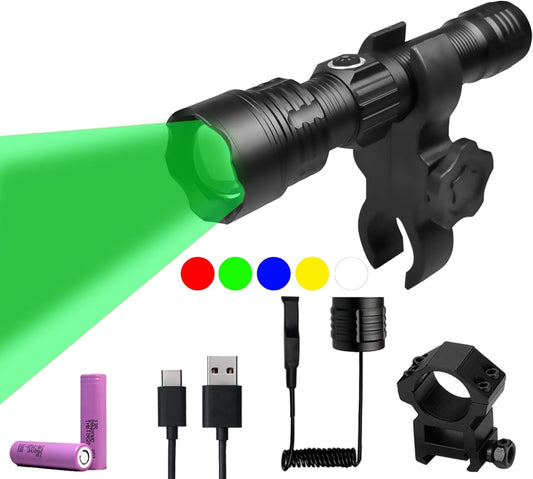
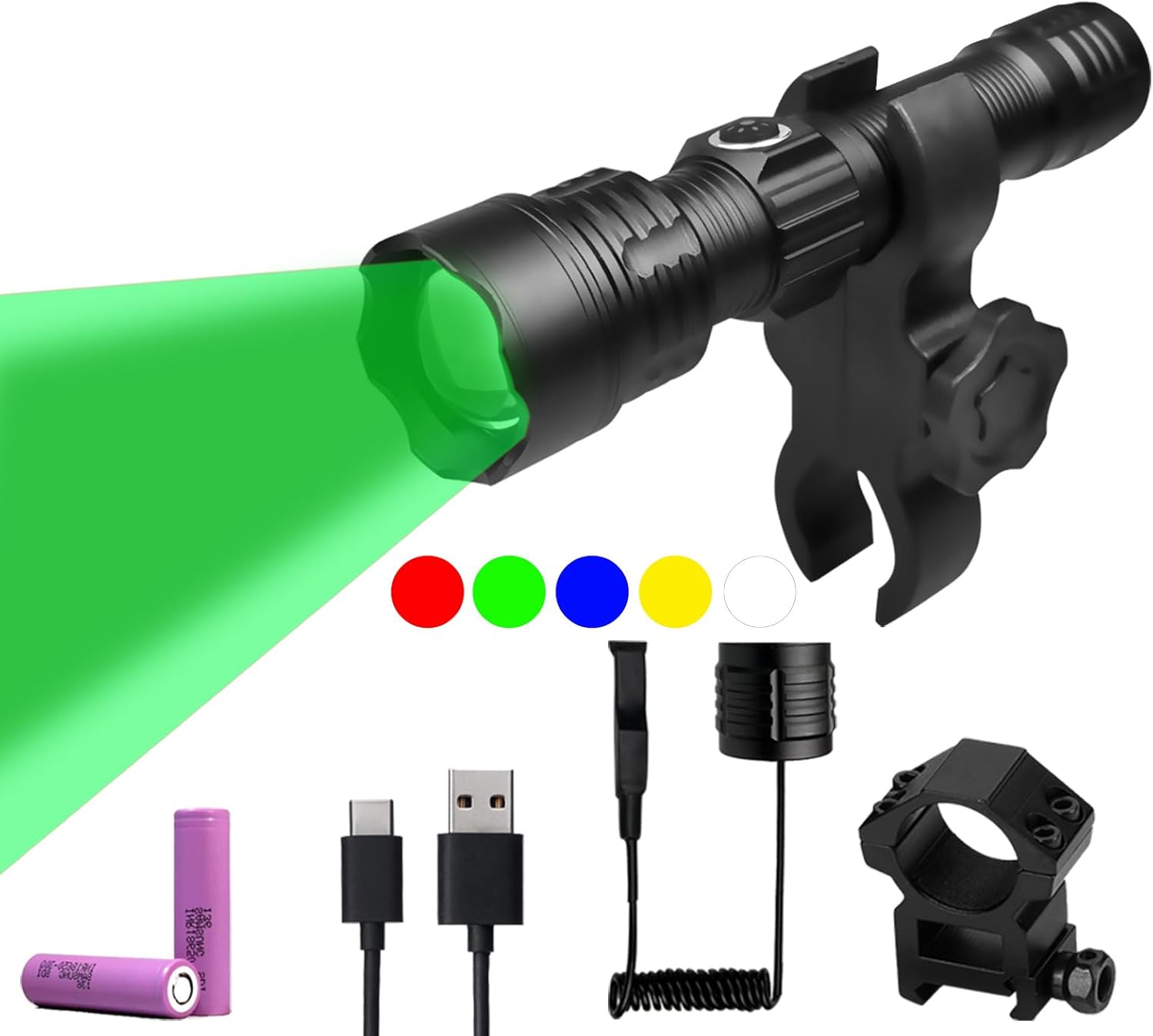
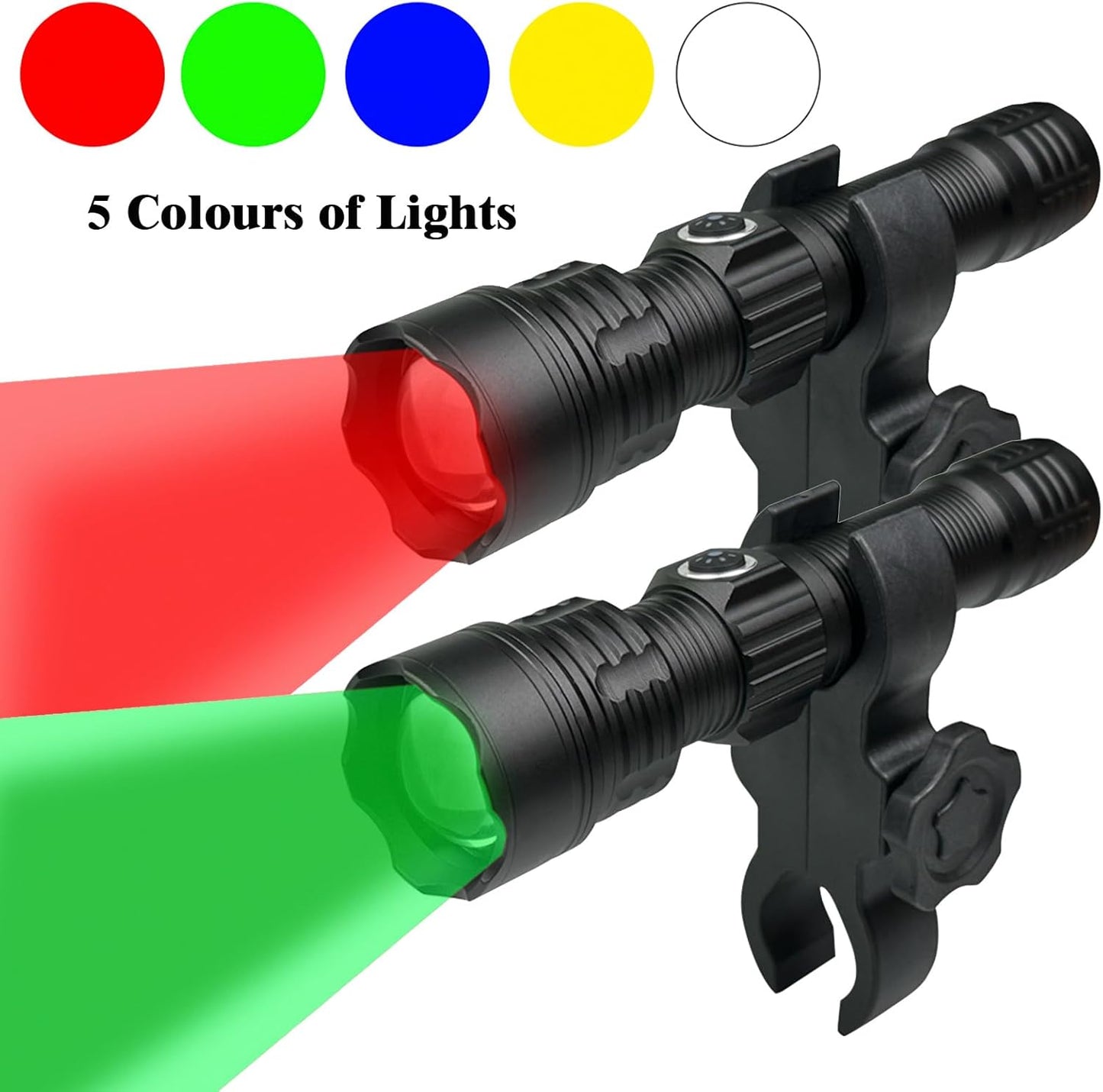
Green Light for Hunting Hog Green Flashlight,Red,Blue,White 4 in 1 Light for Coyote,Hog,Coon,Predator,Varmint,Sniper,Scope,Hunting Lights (Hog Green Light)
通常価格 $79.99通常価格単価 / あたり$199.99セール価格 $79.99セール -
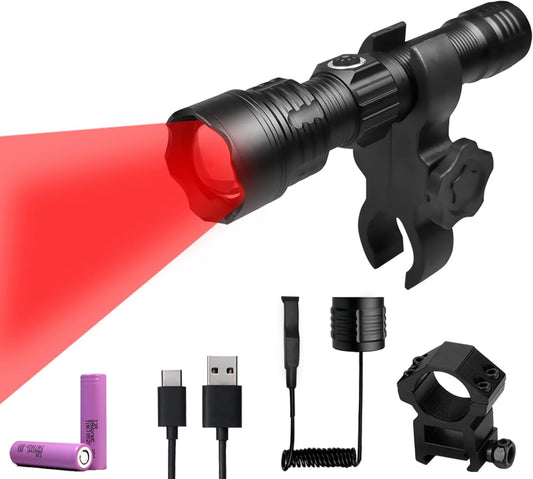
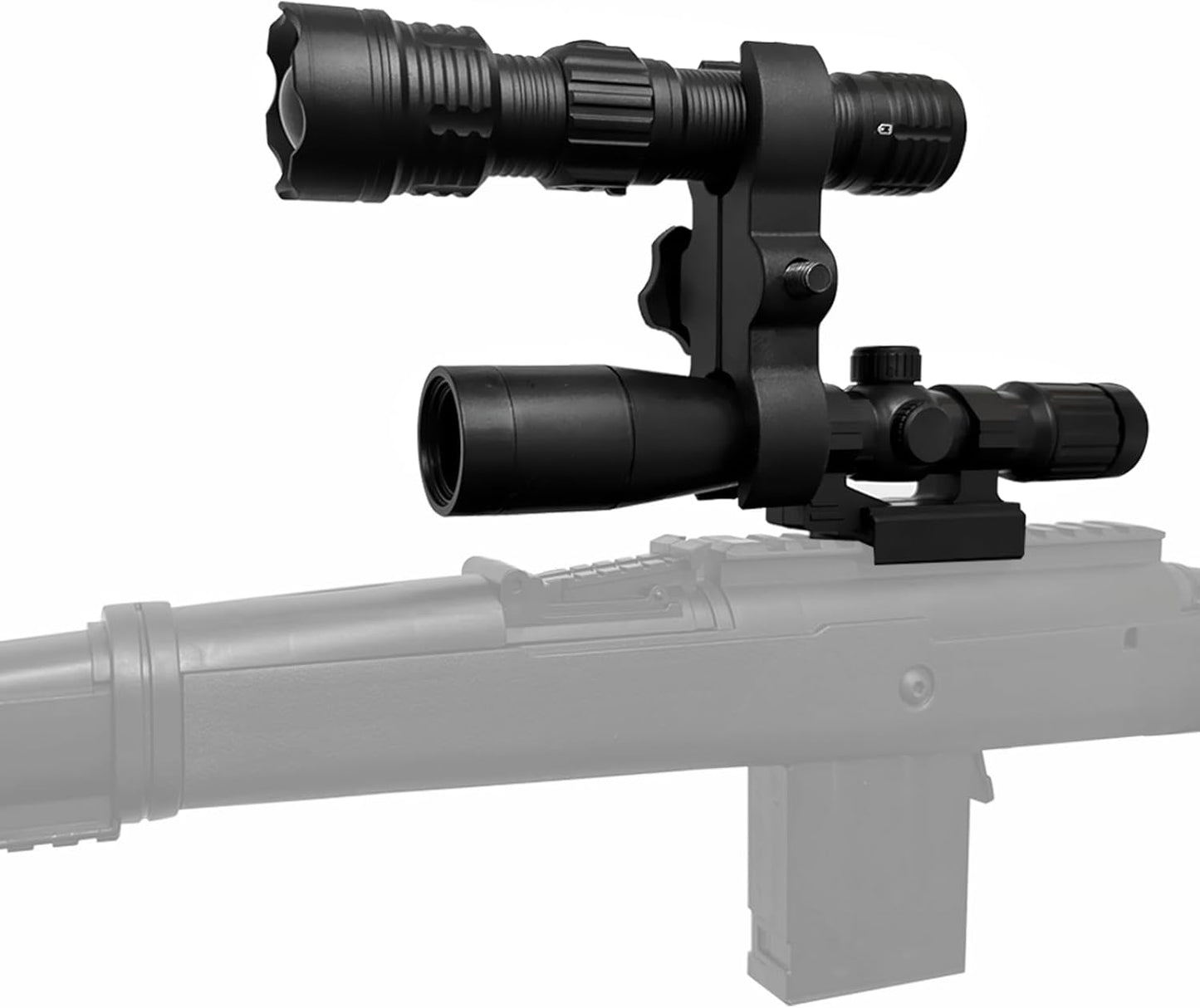
Coyote Hunting Light,Red Light for Hunting,Red,Green,Blue,White 4 in 1 Light for Coyote,Hog,Coon,Predator,Sniper,Scope,Hunting Lights
通常価格 $79.99通常価格単価 / あたり$199.99セール価格 $79.99セール -
Cordless Wood's Lamp Ringworm Detection Light-Skin Testing-Esthetician-Veterinaria-5x Magnifying Wood Lamp Black Light-16 LED-Battery Powered Polarized Skin Dermatology Dermascope Light
通常価格 $49.99通常価格単価 / あたり$99.99セール価格 $49.99セール -
Best Rechargeable Blood Tracking Flashlight for Hunting Deer Blood Trail Finder At Night Perfect for Wounded Game Tracking-Hunters Gifts
通常価格 $39.99通常価格単価 / あたり$69.99セール価格 $39.99セール -
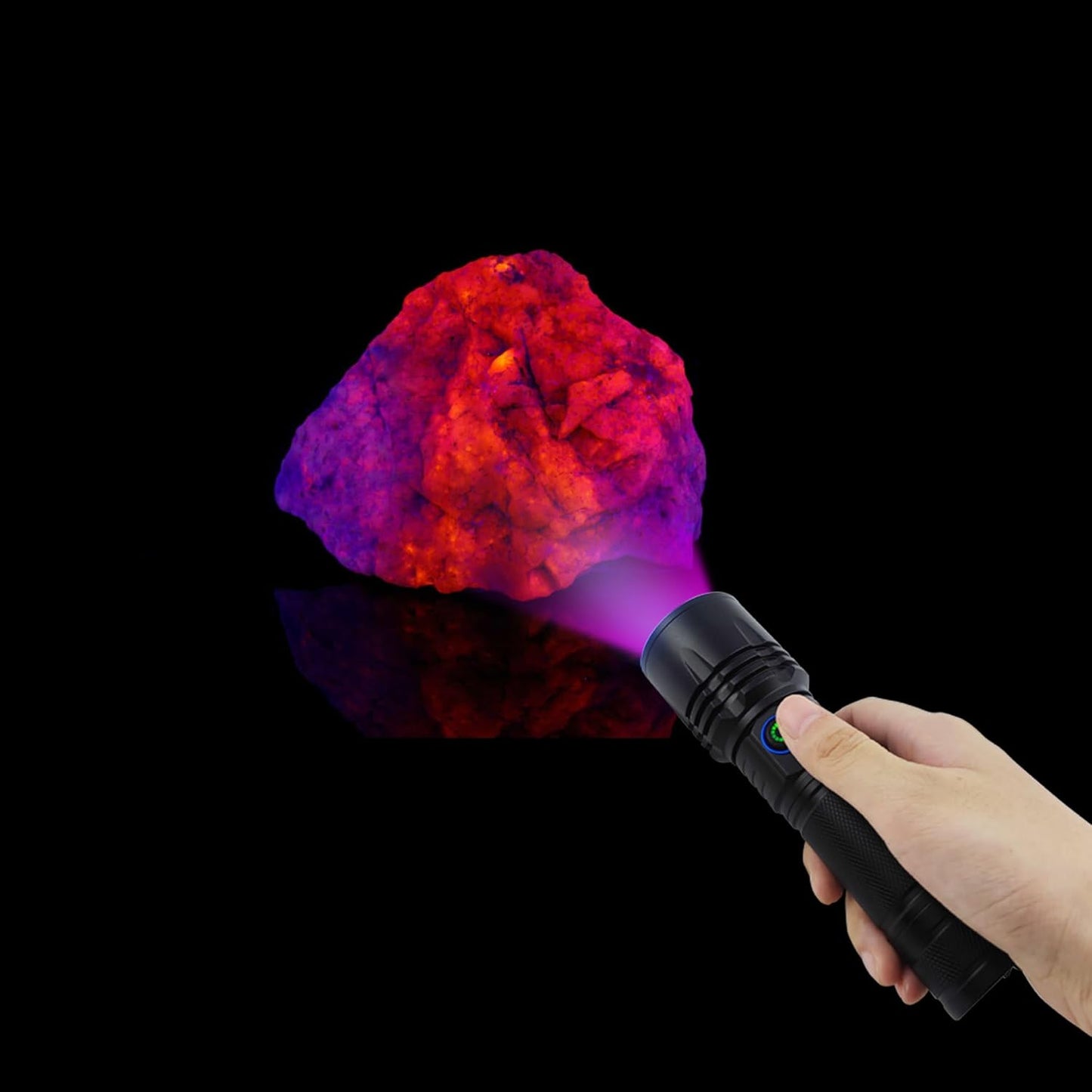
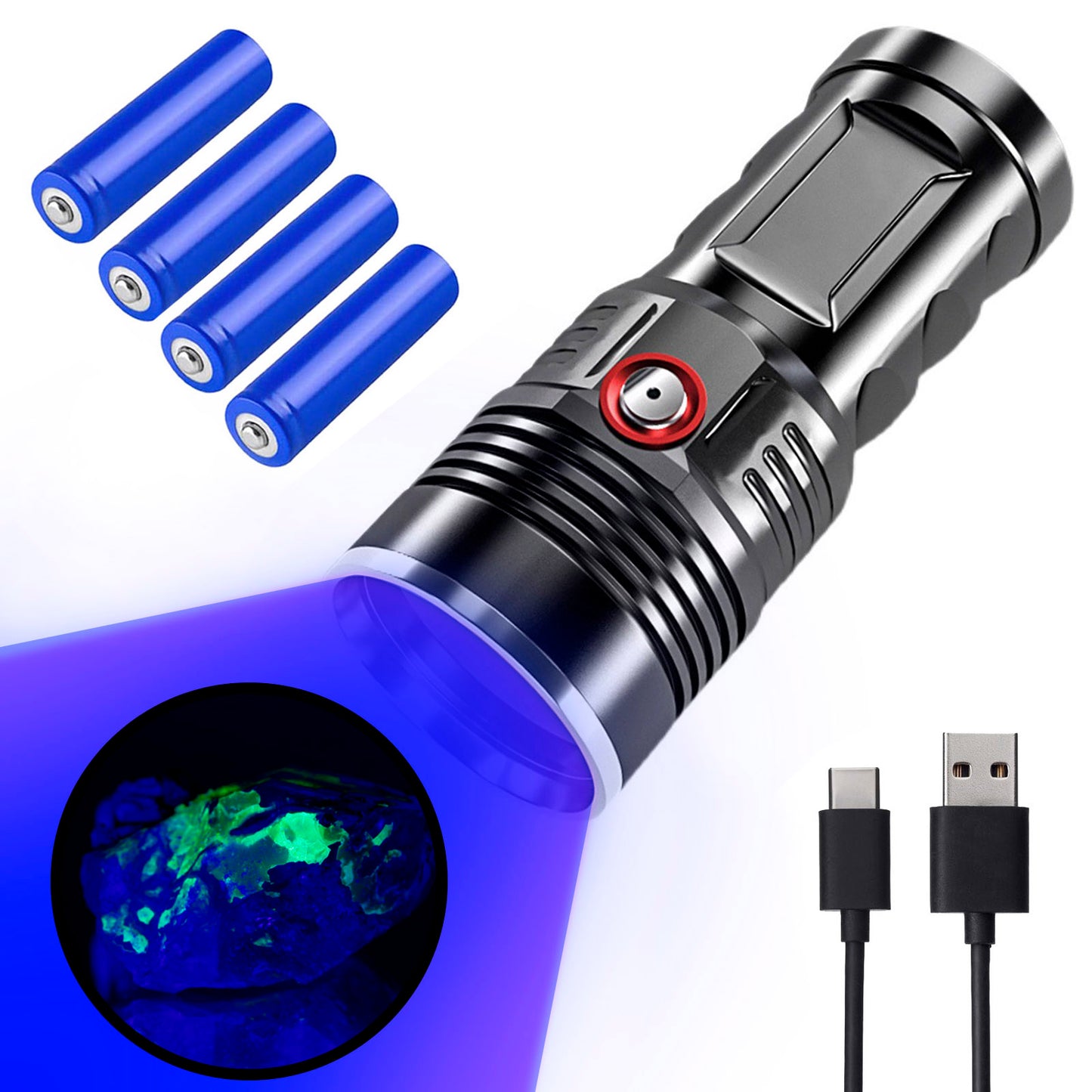
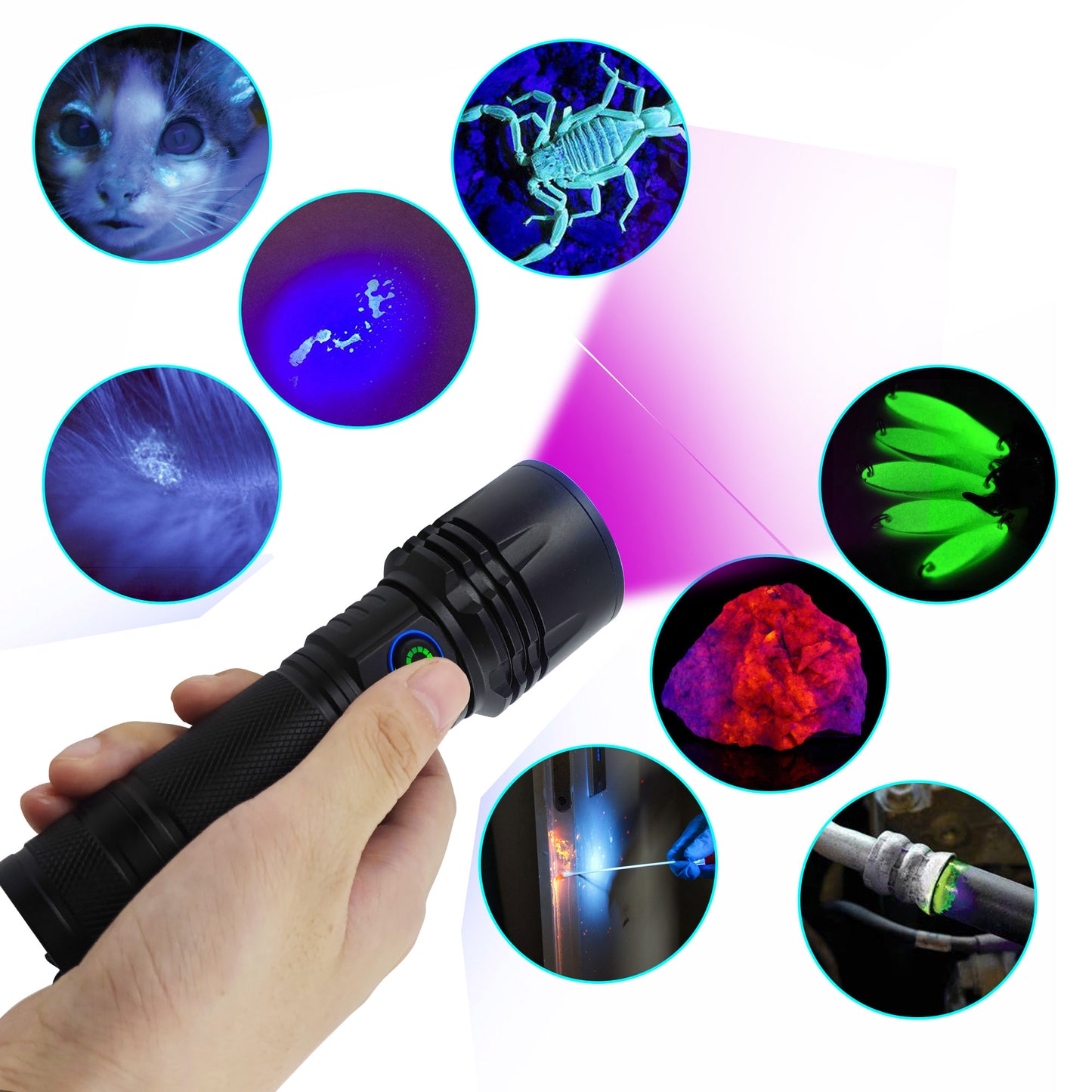
365nm UV Flashlight for Rock Hunting & Mineral Detection - Professional Gemstone Detector Tool with High Power Short/Long Wave, Portable UV Light for Crystals, Agates, Uranium Glass, Jade Appraisal
通常価格 $29.99から通常価格単価 / あたり$79.99セール価格 $29.99からセール
1
/
の
10