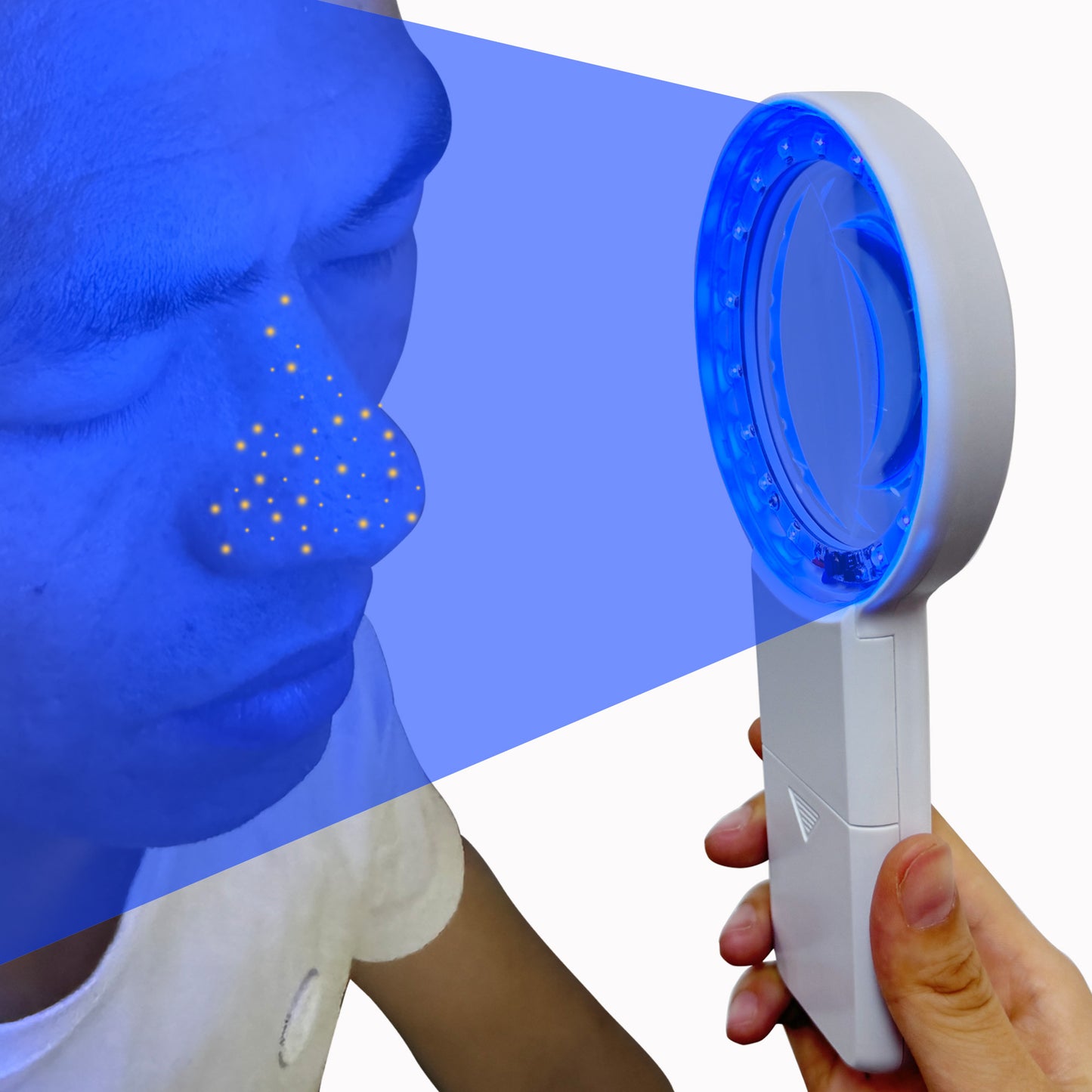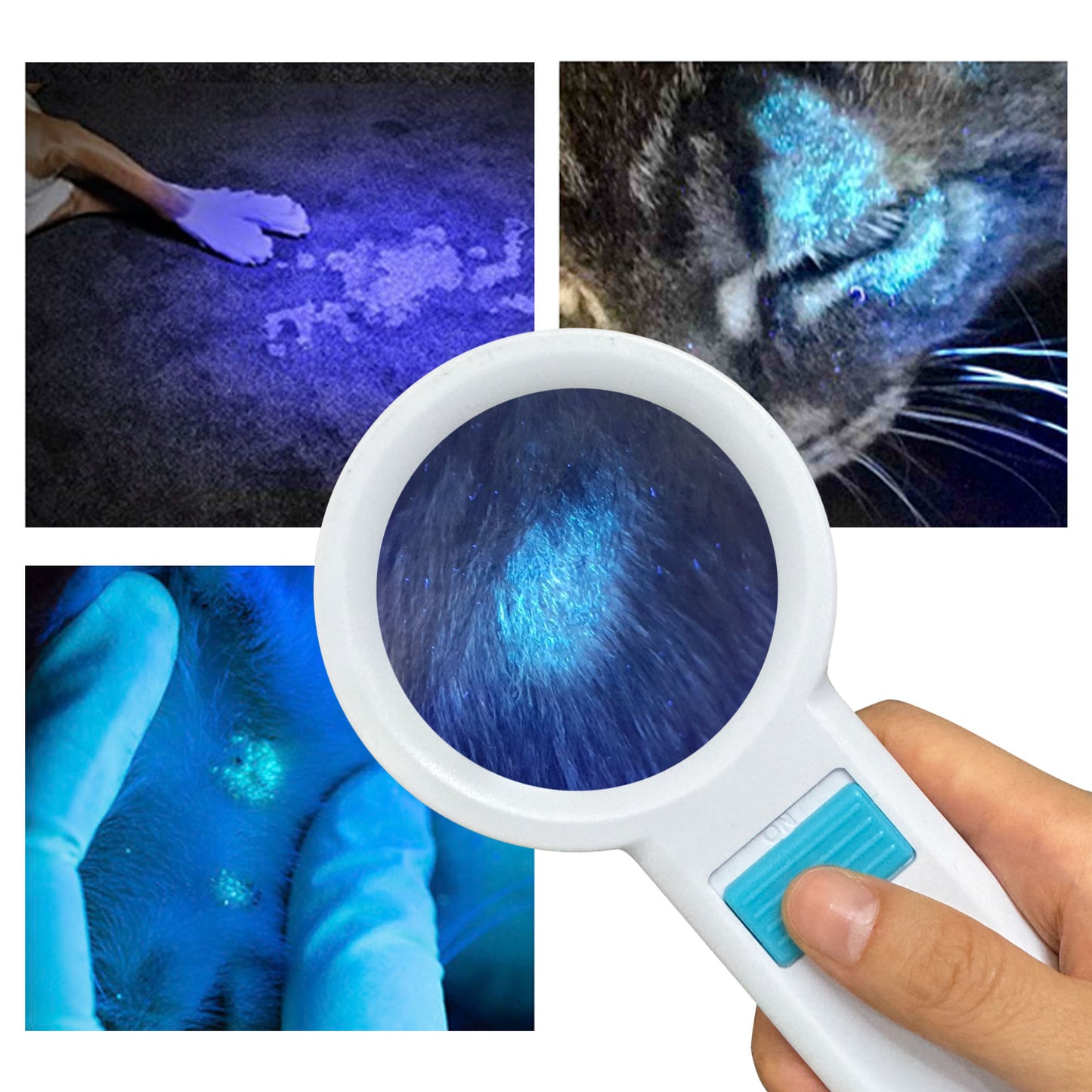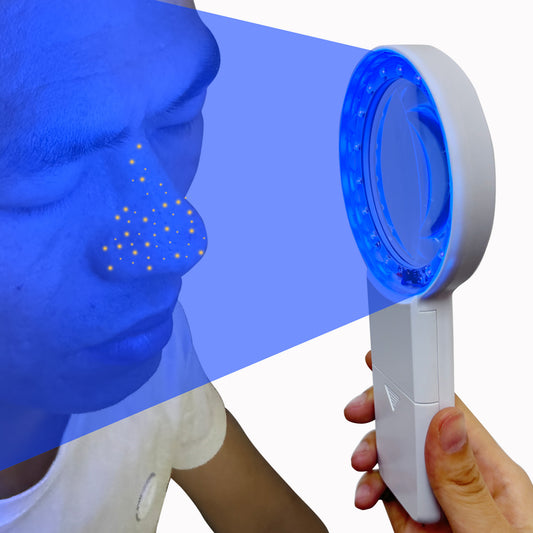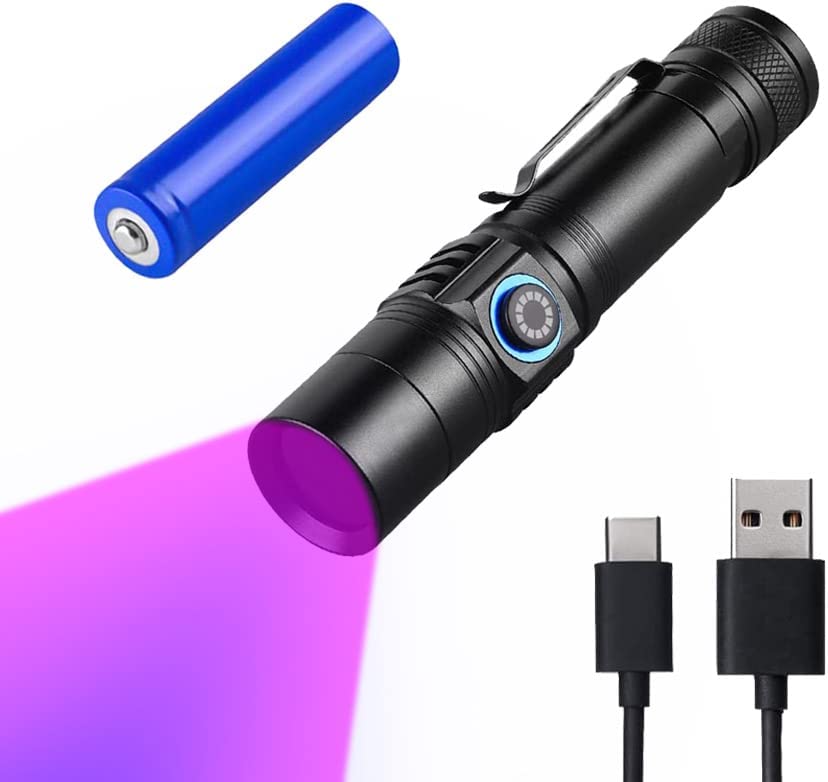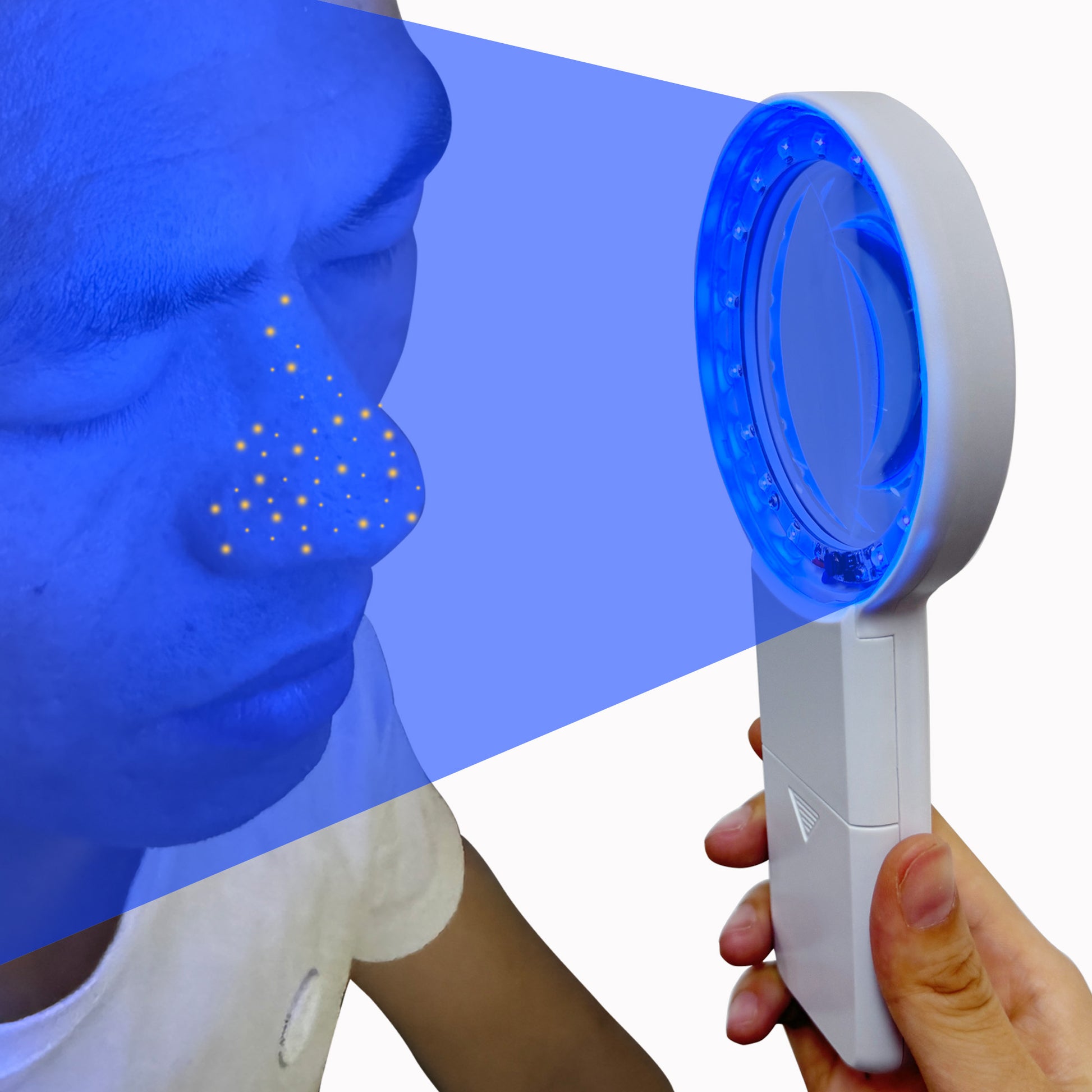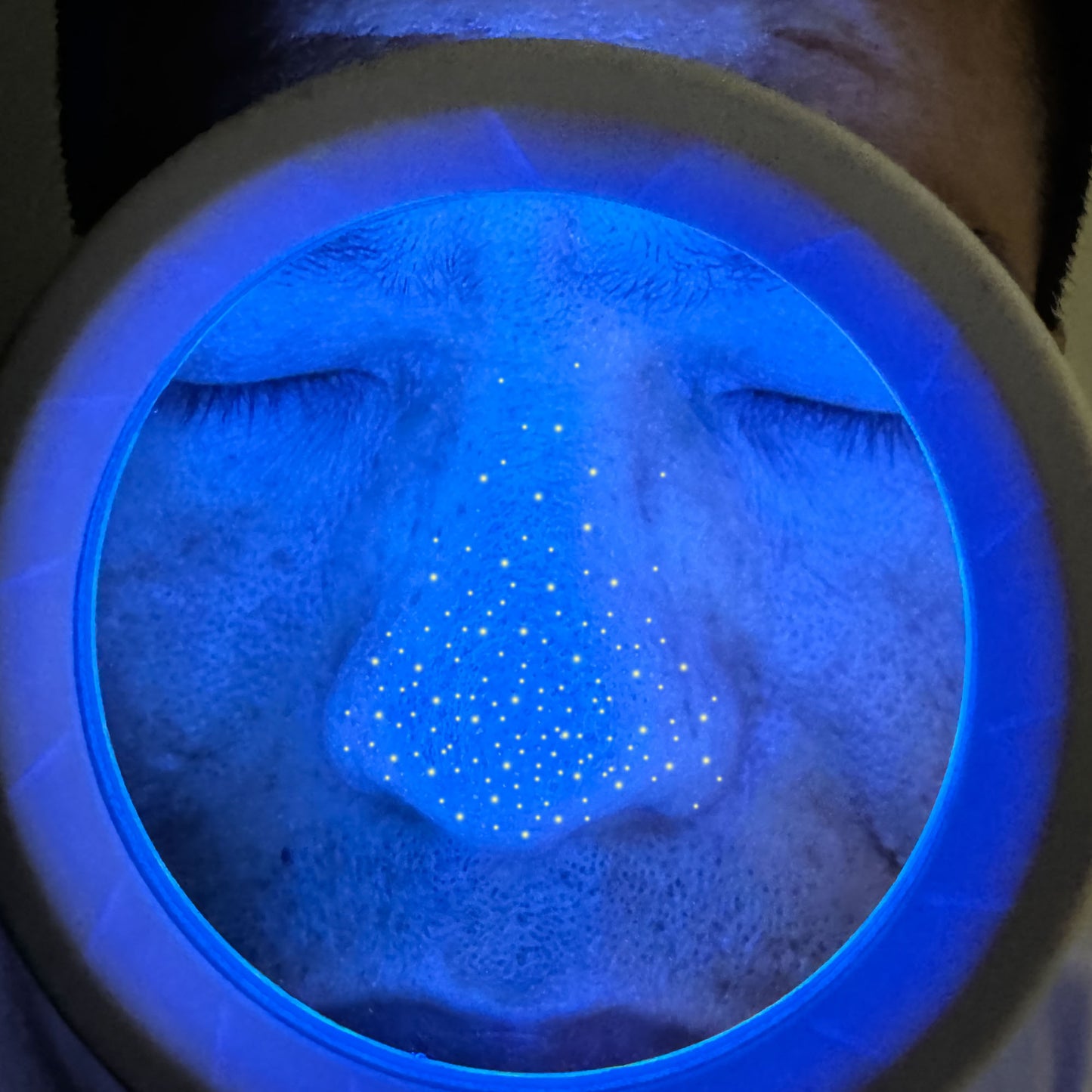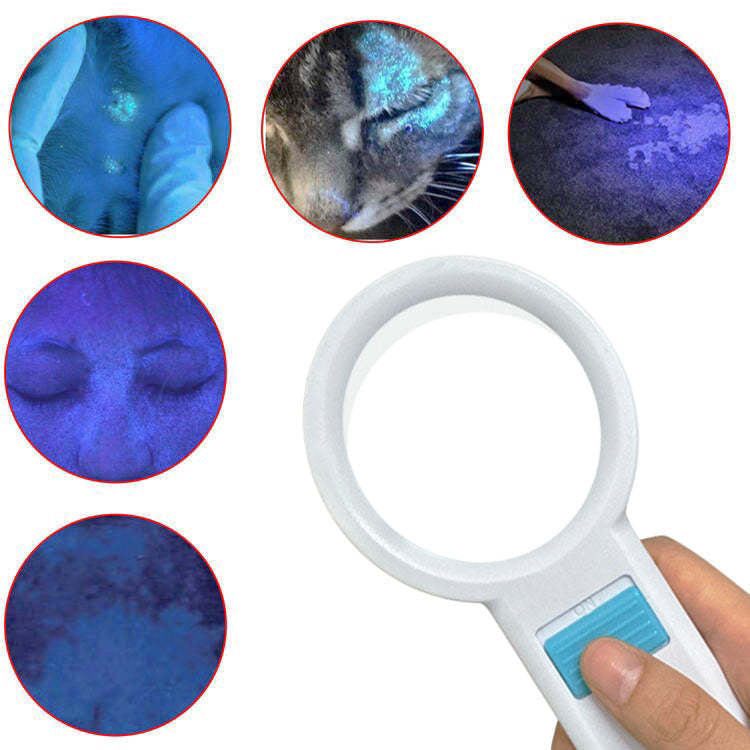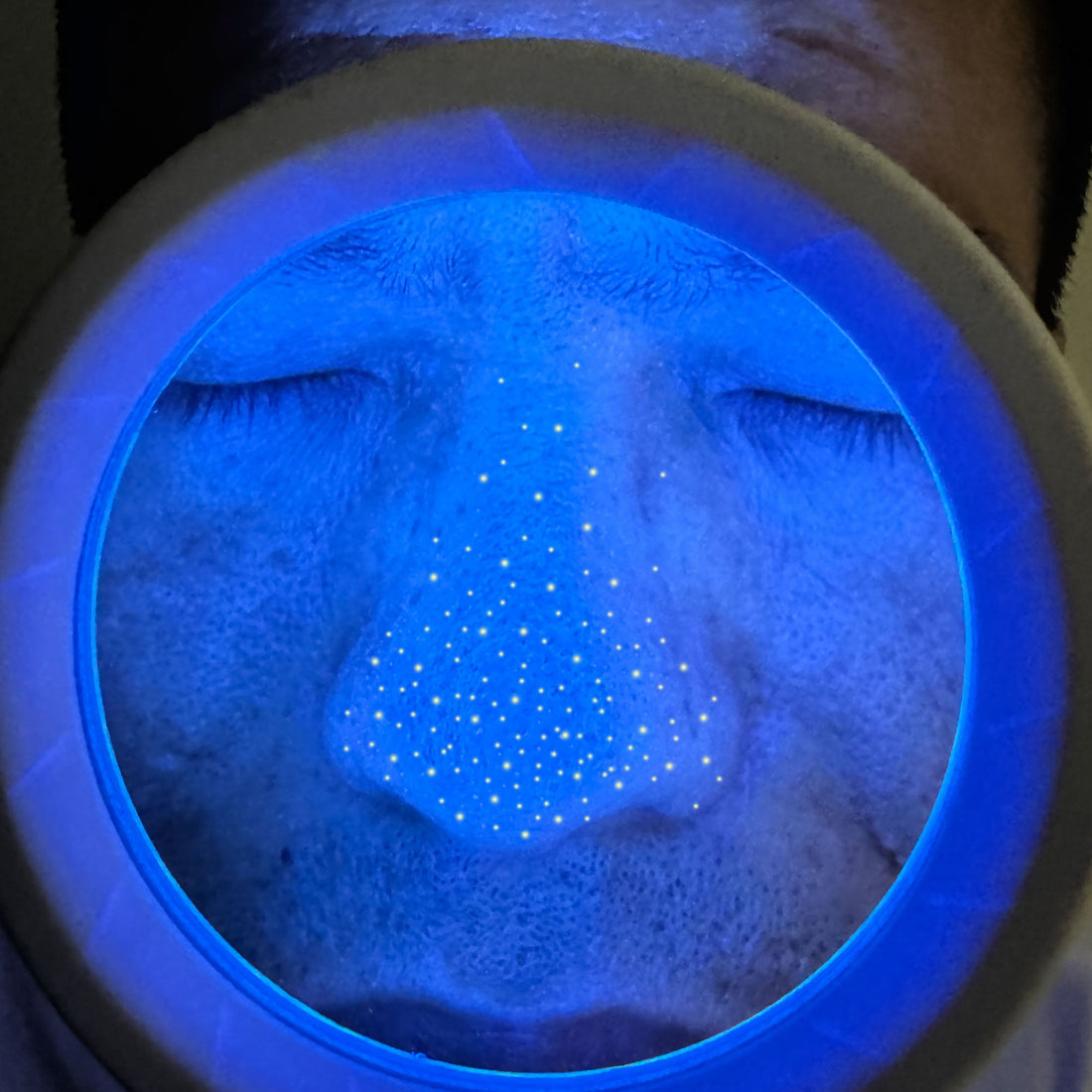

What skin conditions can a Woods lamp help diagnose?
Video
Featured collection
-
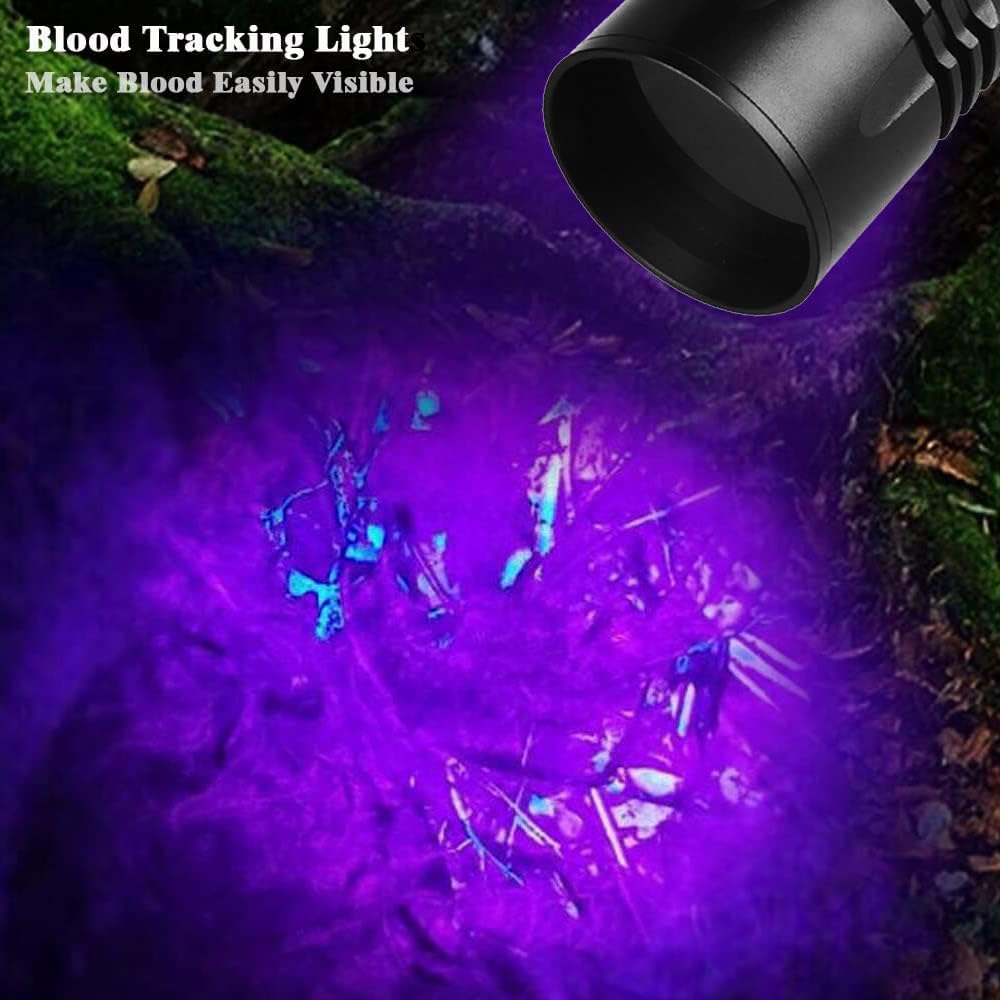
Uv Blood Tracking Flashlight for Hunting Deer Finder Blood Trailing Light Rechargeable Blood Tracker Light
Precio habitual A partir de $29.99Precio habitualPrecio unitario / por$79.99Precio de oferta A partir de $29.99Oferta -
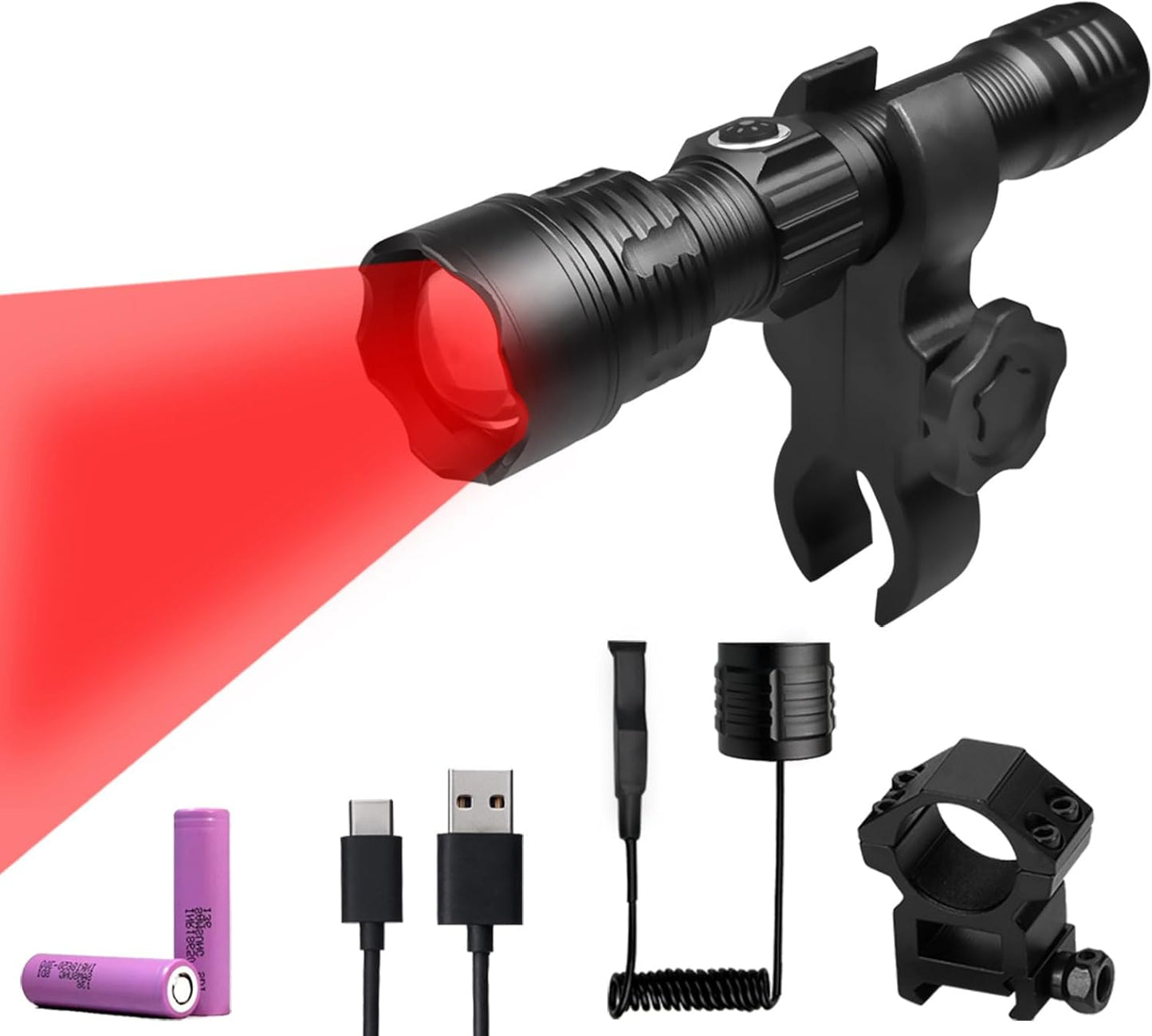
Rechargeable Blood Tracking Light for Night Hunting 2000 Lumens Blood Trail Tracking Flashlight Gifts for Hunter (Blood Finder Light)
Precio habitual $39.99Precio habitualPrecio unitario / por$69.99Precio de oferta $39.99Oferta -
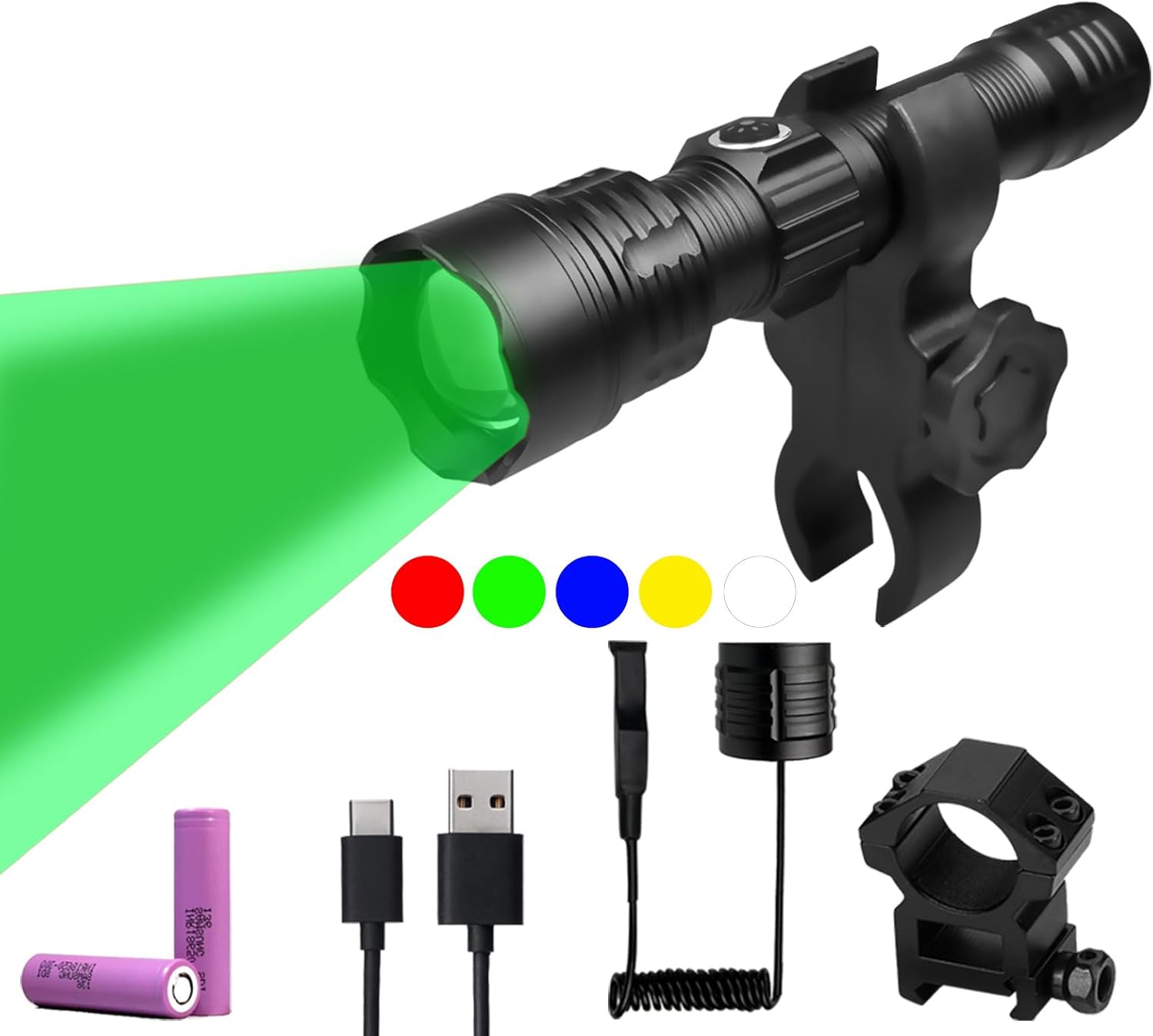
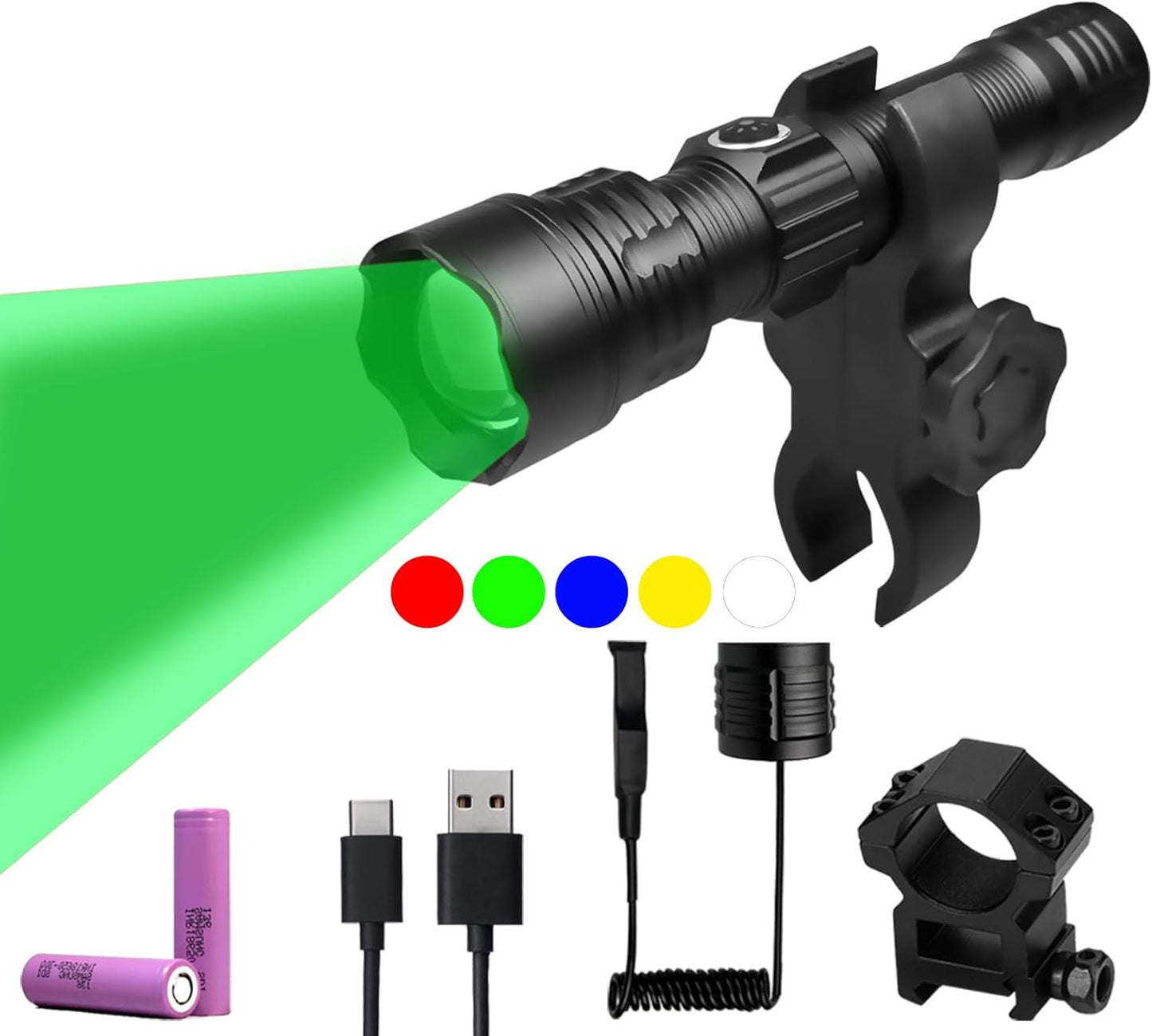
Green Light for Hunting Hog Green Flashlight,Red,Blue,White 4 in 1 Light for Coyote,Hog,Coon,Predator,Varmint,Sniper,Scope,Hunting Lights (Hog Green Light)
Precio habitual $79.99Precio habitualPrecio unitario / por$199.99Precio de oferta $79.99Oferta -
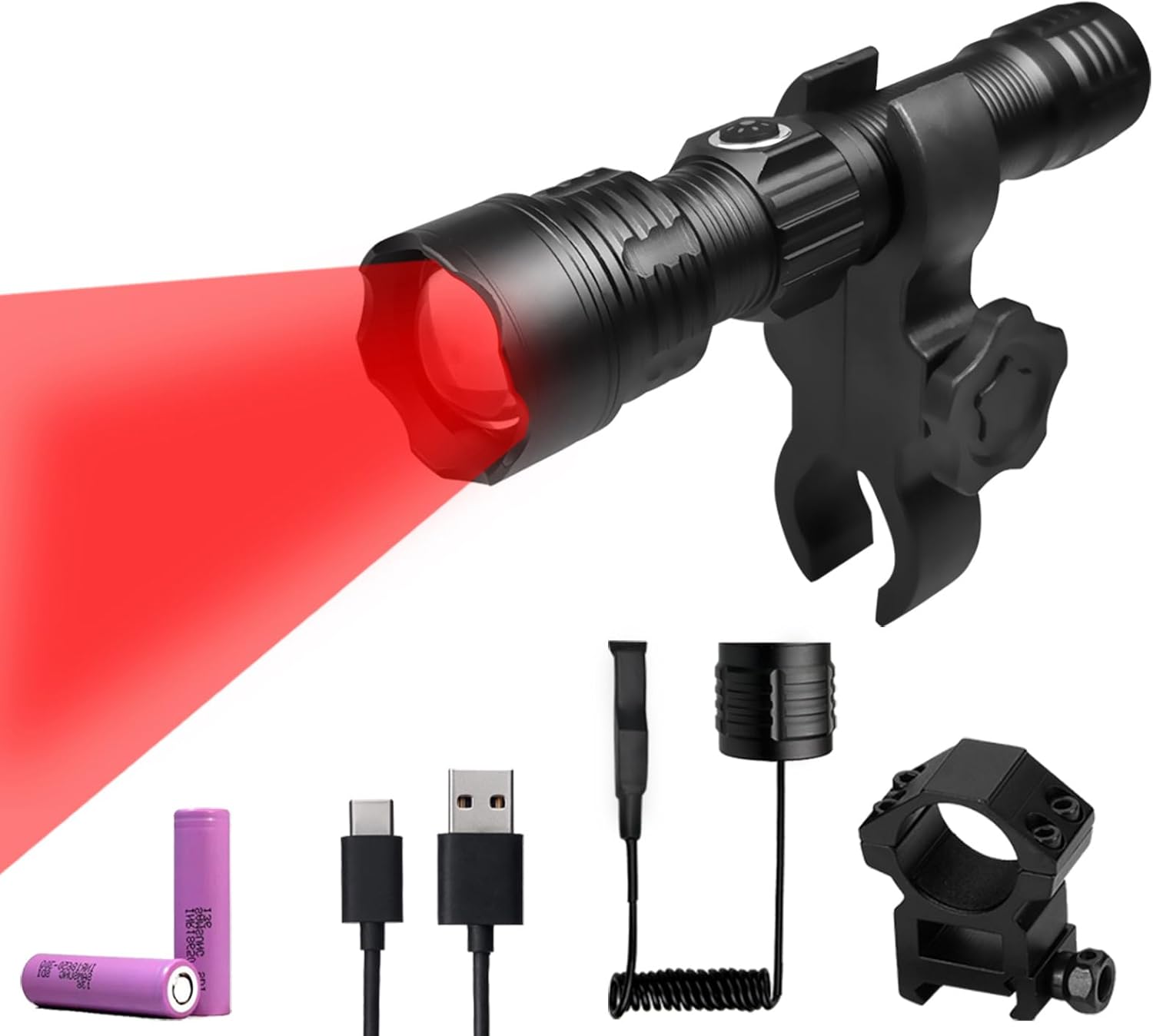
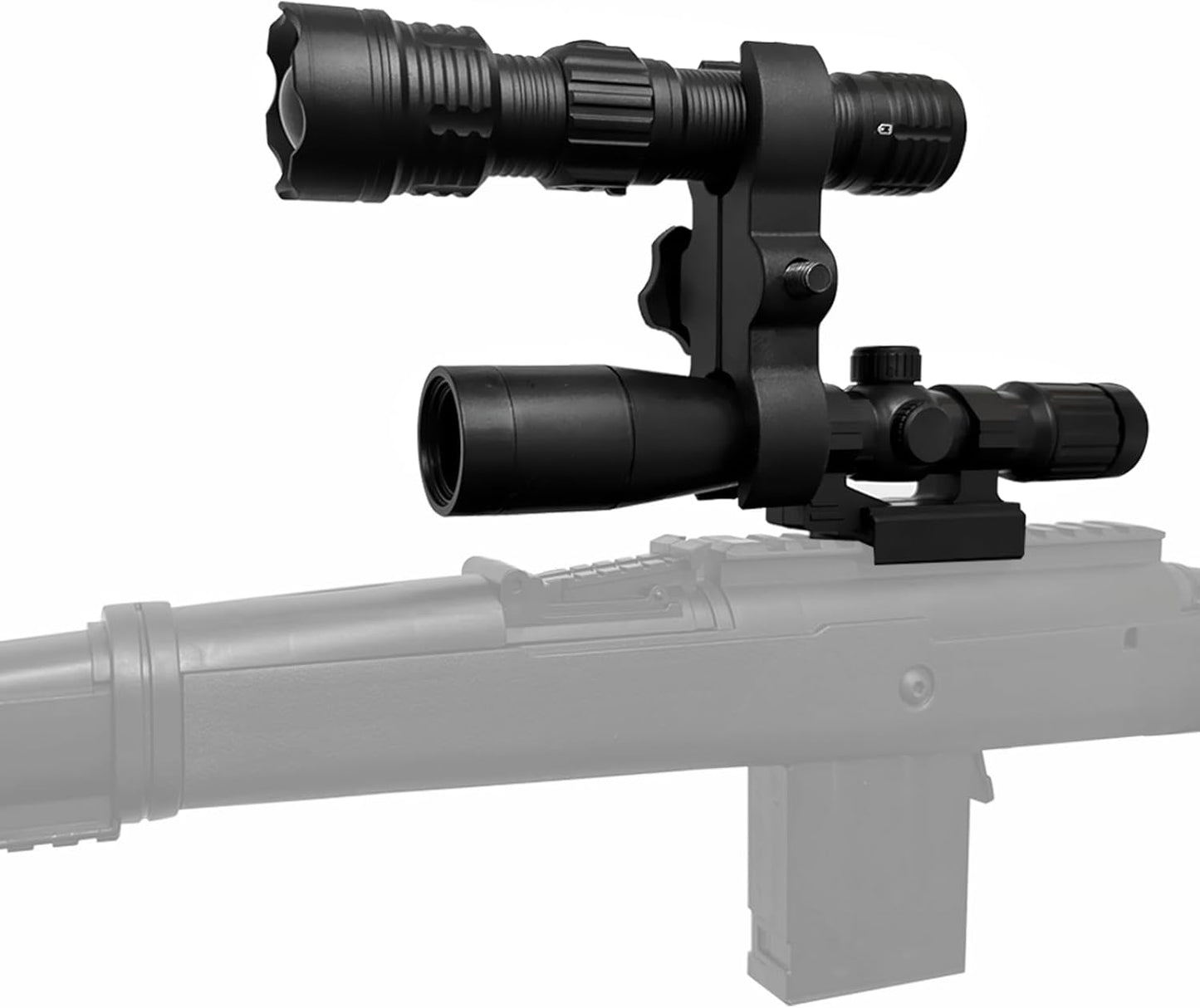
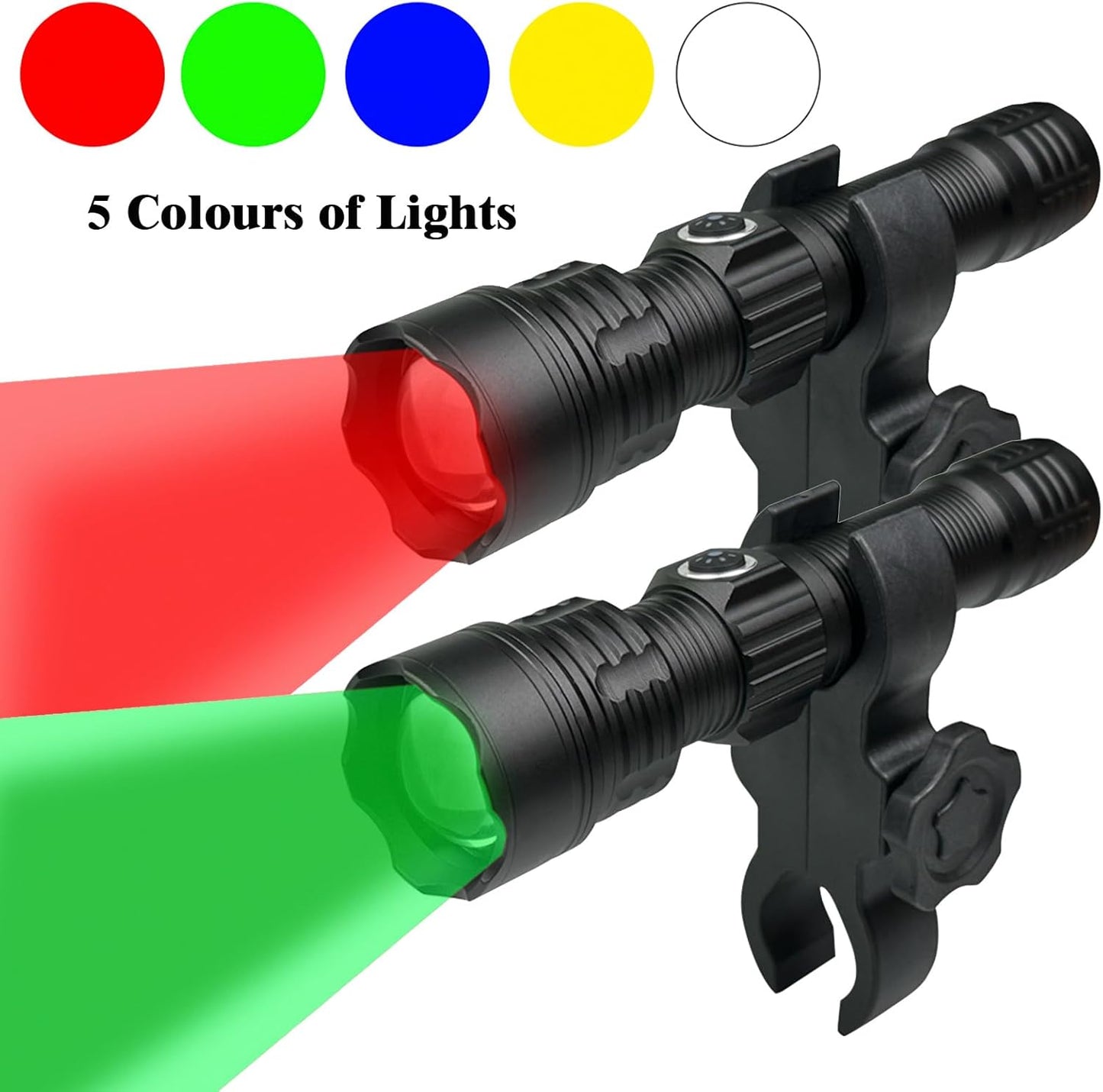
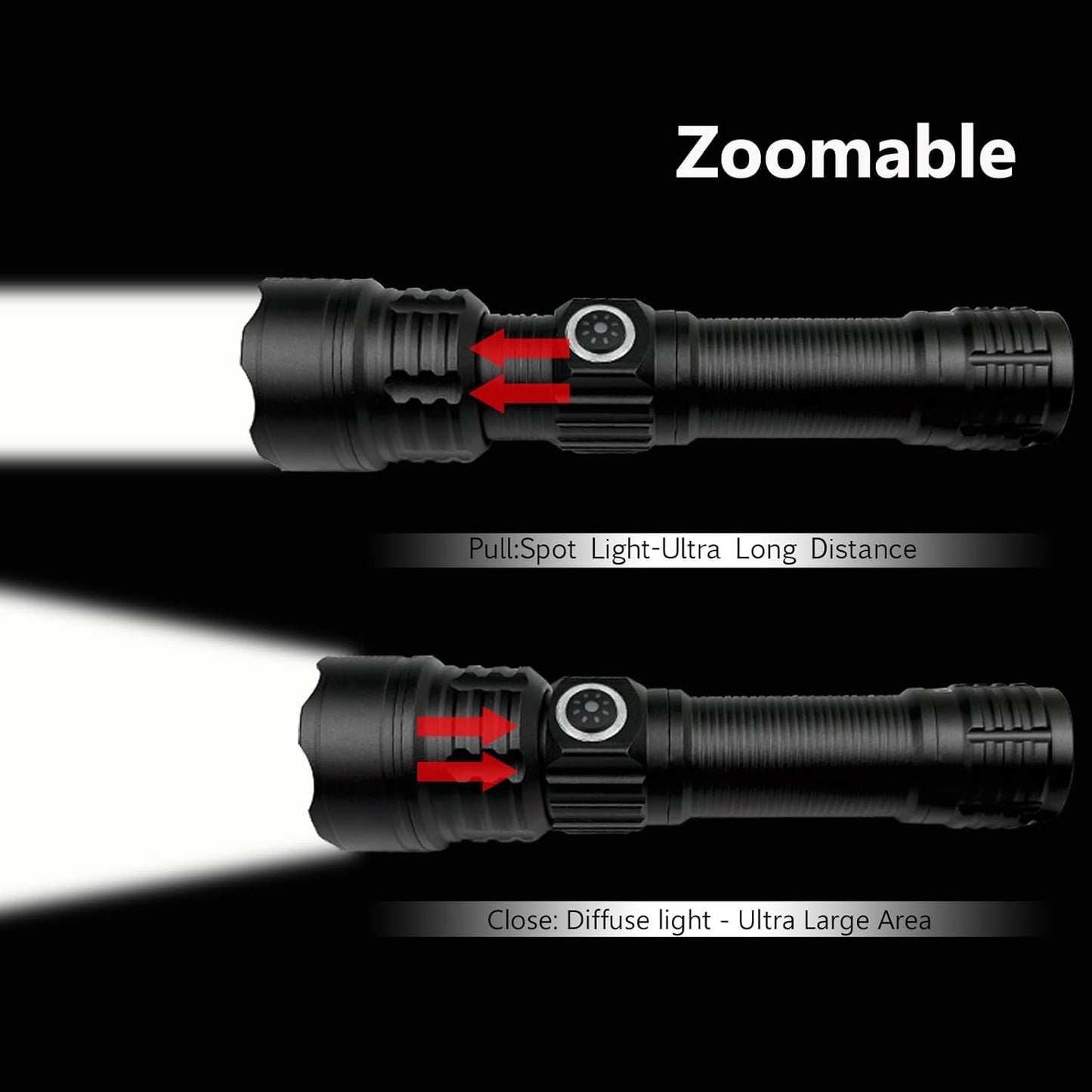
Coyote Hunting Light,Red Light for Hunting,Red,Green,Blue,White 4 in 1 Light for Coyote,Hog,Coon,Predator,Sniper,Scope,Hunting Lights
Precio habitual $79.99Precio habitualPrecio unitario / por$199.99Precio de oferta $79.99Oferta -
Cordless Wood's Lamp Ringworm Detection Light-Skin Testing-Esthetician-Veterinaria-5x Magnifying Wood Lamp Black Light-16 LED-Battery Powered Polarized Skin Dermatology Dermascope Light
Precio habitual $49.99Precio habitualPrecio unitario / por$99.99Precio de oferta $49.99Oferta -
Best Rechargeable Blood Tracking Flashlight for Hunting Deer Blood Trail Finder At Night Perfect for Wounded Game Tracking-Hunters Gifts
Precio habitual $39.99Precio habitualPrecio unitario / por$69.99Precio de oferta $39.99Oferta -
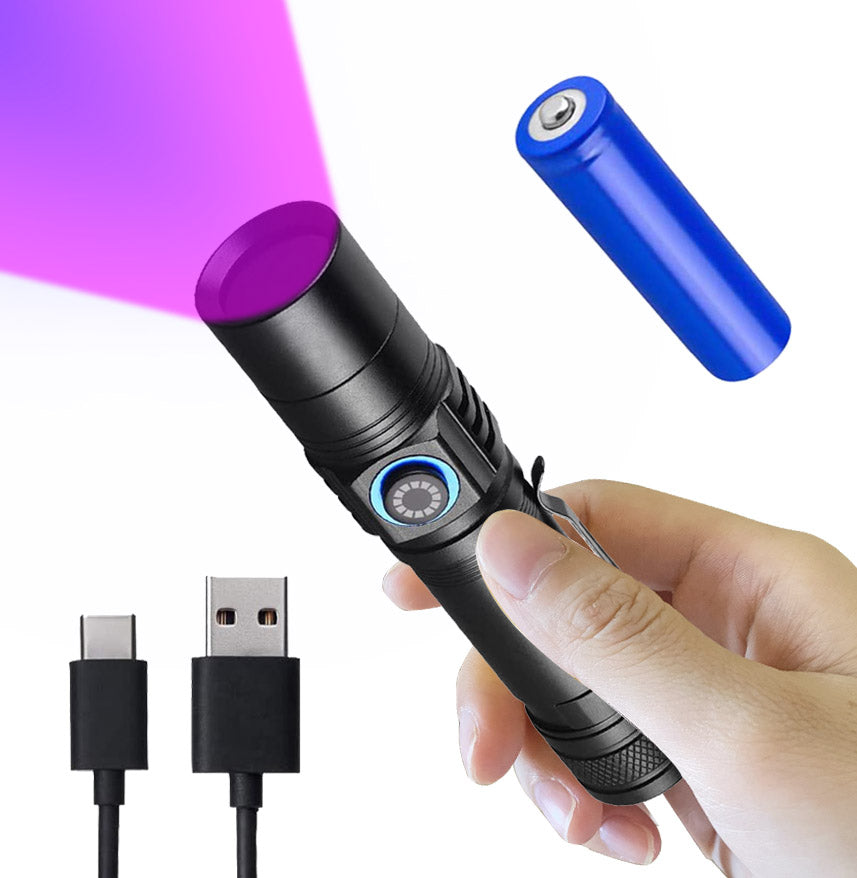
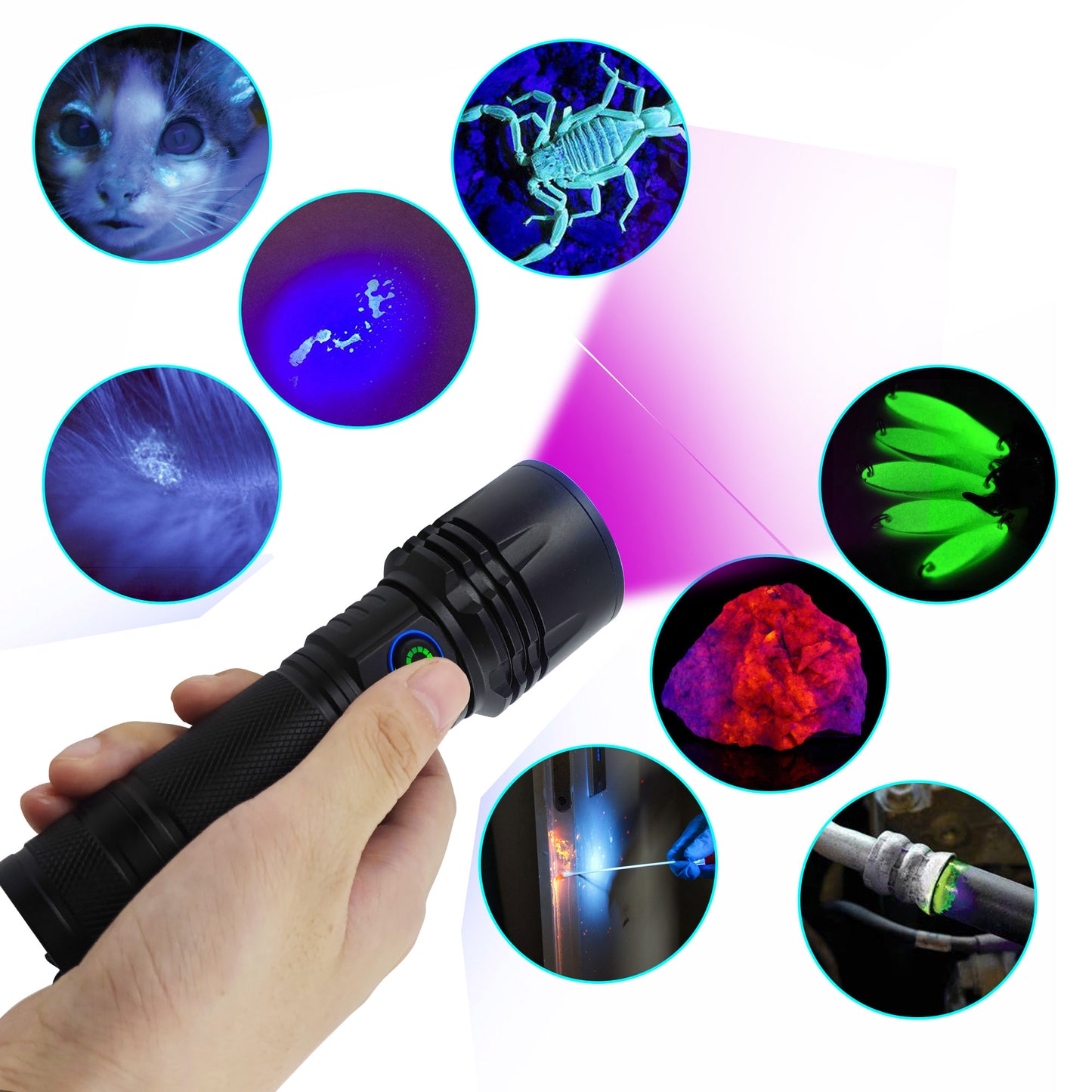
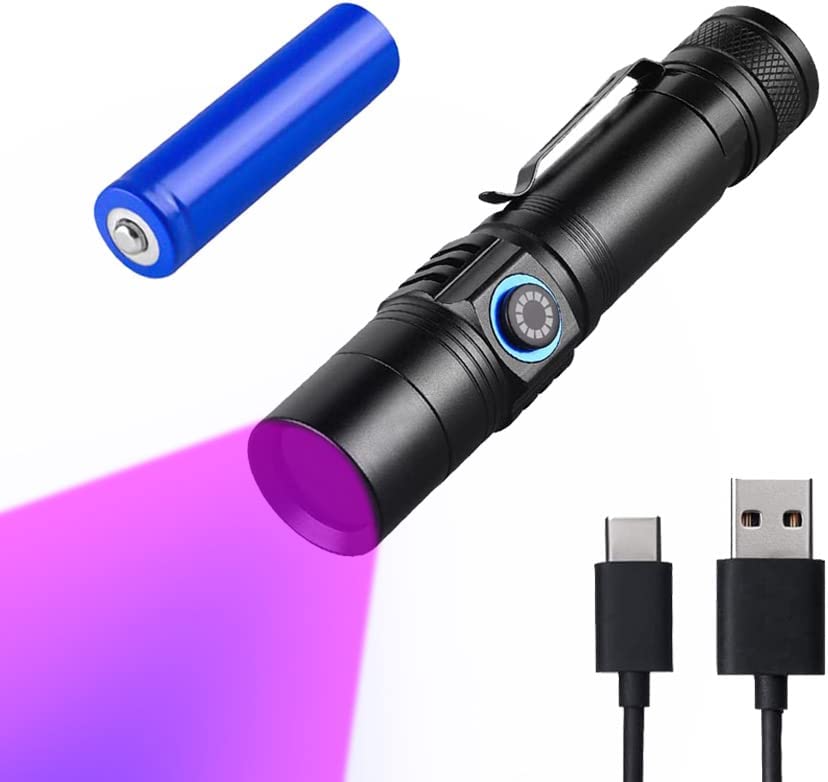
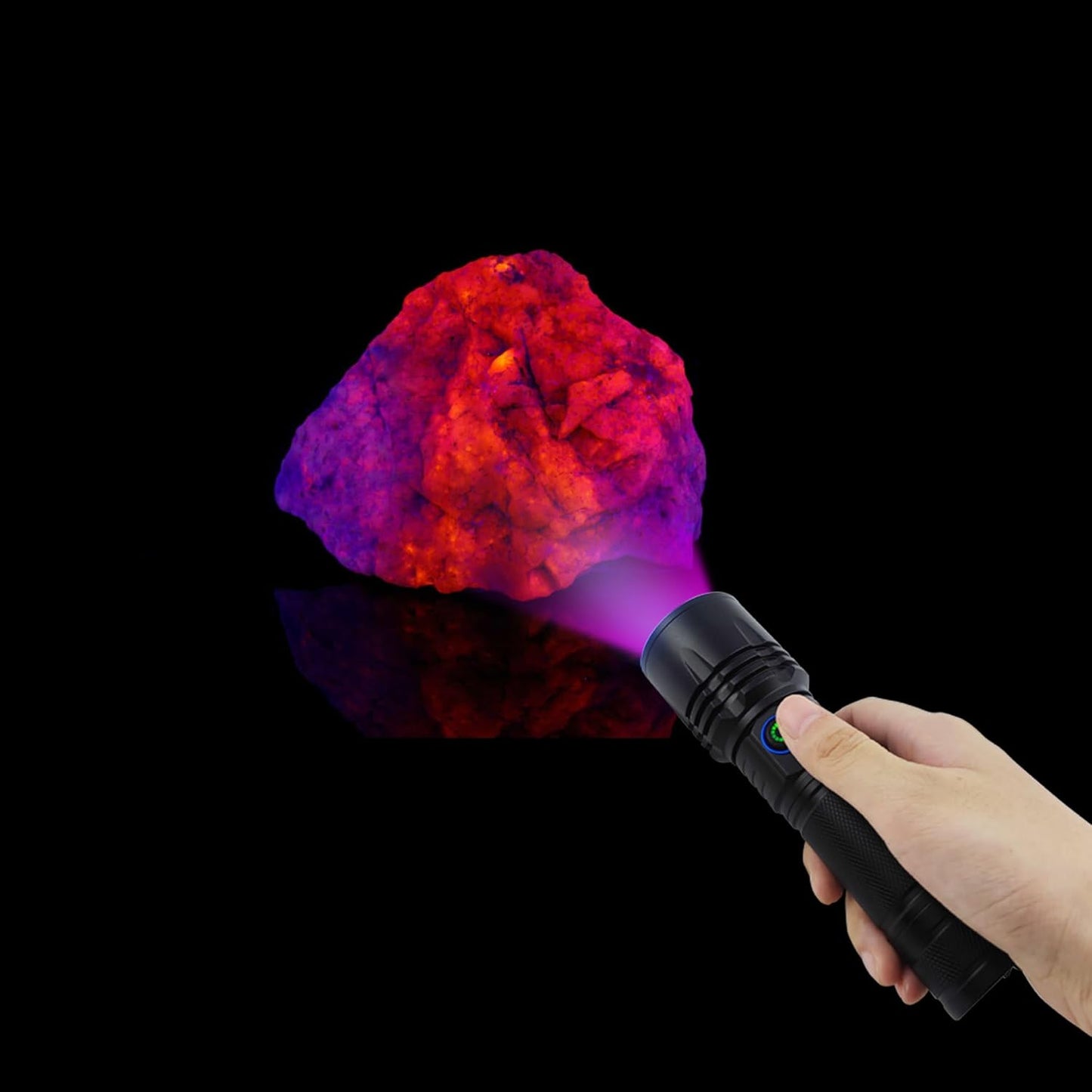
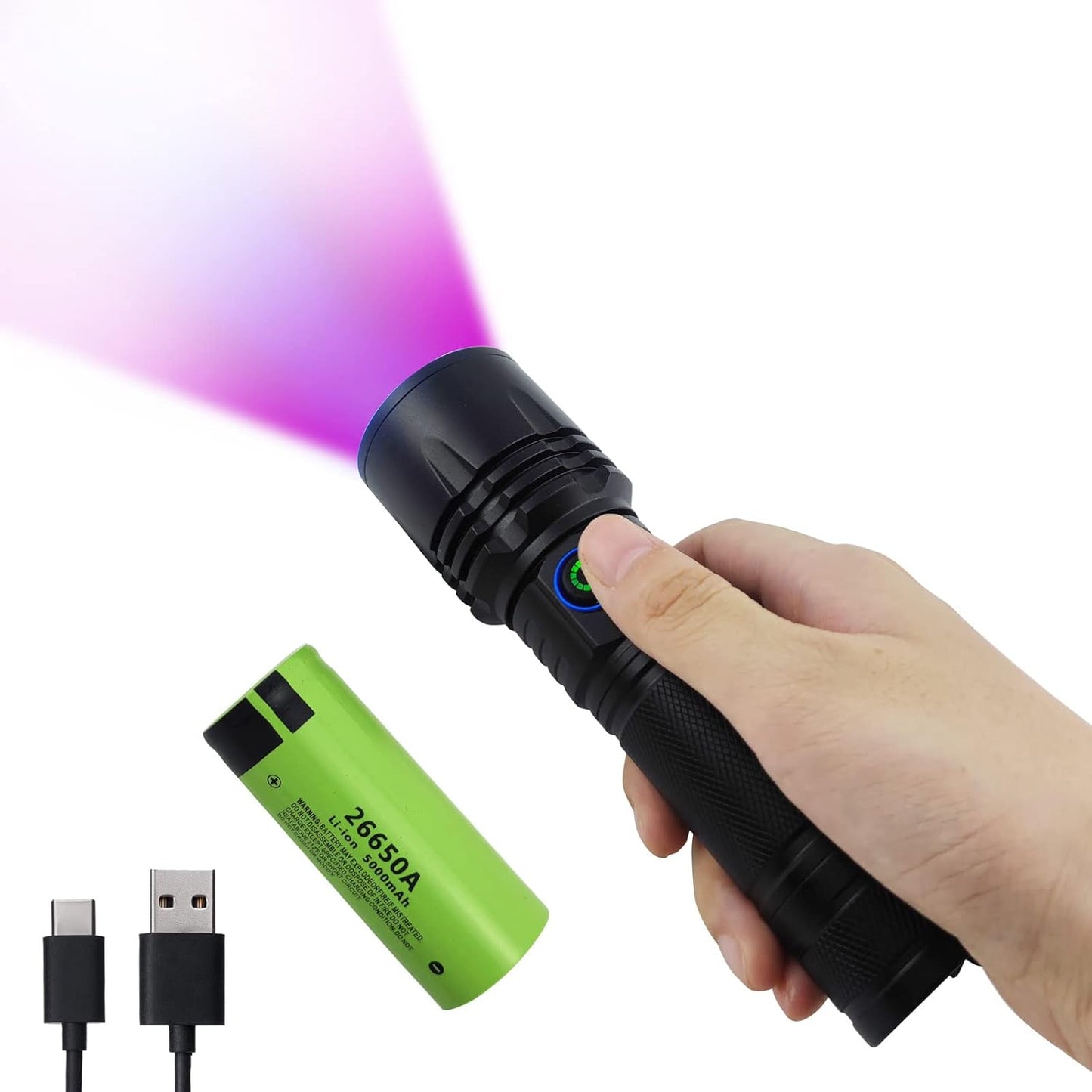
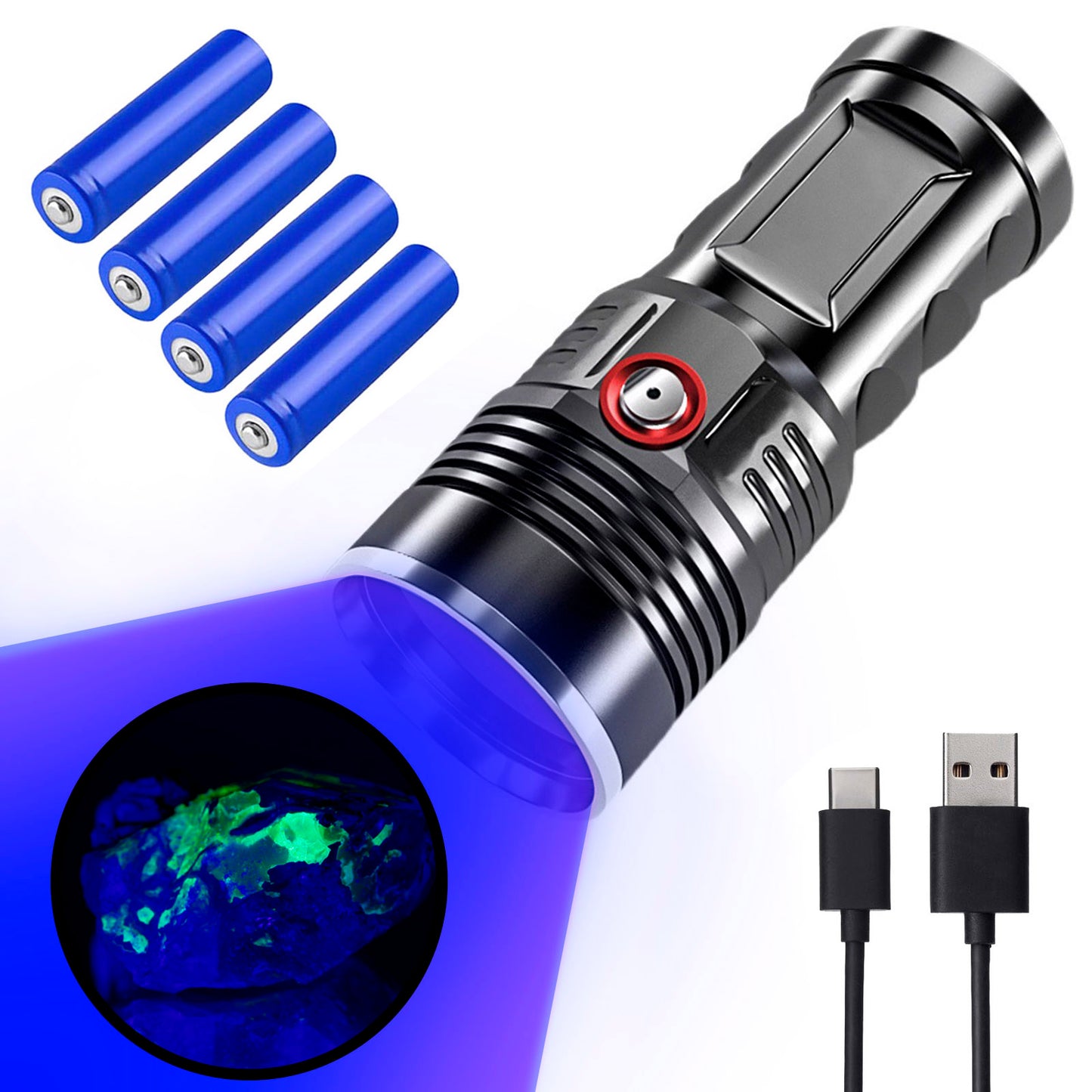
365nm UV Flashlight for Rock Hunting & Mineral Detection - Professional Gemstone Detector Tool with High Power Short/Long Wave, Portable UV Light for Crystals, Agates, Uranium Glass, Jade Appraisal
Precio habitual A partir de $29.99Precio habitualPrecio unitario / por$79.99Precio de oferta A partir de $29.99Oferta
I0D0
Rechargeable Blood Tracking Light for Night Hunting 2000 Lumens Blood Trail Tracking Flashlight Gifts for Hunter (Blood Finder Light)
Precio habitual
$39.99
Precio habitual
$69.99
Precio de oferta
$39.99
Precio unitario
/
por
Los gastos de envío se calculan en la pantalla de pago.
Share
I0D0
Uv Blood Tracking Flashlight for Hunting Deer Finder Blood Trailing Light Rechargeable Blood Tracker Light
Precio habitual
$29.99
Precio habitual
$79.99
Precio de oferta
$29.99
Precio unitario
/
por
Los gastos de envío se calculan en la pantalla de pago.
Share








I0D0
Green Light for Hunting Hog Green Flashlight,Red,Blue,White 4 in 1 Light for Coyote,Hog,Coon,Predator,Varmint,Sniper,Scope,Hunting Lights (Hog Green Light)
Precio habitual
$79.99
Precio habitual
$199.99
Precio de oferta
$79.99
Precio unitario
/
por
Los gastos de envío se calculan en la pantalla de pago.
Share







I0D0
Coyote Hunting Light,Red Light for Hunting,Red,Green,Blue,White 4 in 1 Light for Coyote,Hog,Coon,Predator,Sniper,Scope,Hunting Lights
Precio habitual
$79.99
Precio habitual
$199.99
Precio de oferta
$79.99
Precio unitario
/
por
Los gastos de envío se calculan en la pantalla de pago.
Share







I0D0
365nm UV Flashlight for Rock Hunting & Mineral Detection - Professional Gemstone Detector Tool with High Power Short/Long Wave, Portable UV Light for Crystals, Agates, Uranium Glass, Jade Appraisal
Precio habitual
$29.99
Precio habitual
$79.99
Precio de oferta
$29.99
Precio unitario
/
por
Los gastos de envío se calculan en la pantalla de pago.
Share









I0D0
Cordless Wood's Lamp Ringworm Detection Light-Skin Testing-Esthetician-Veterinaria-5x Magnifying Wood Lamp Black Light-16 LED-Battery Powered Polarized Skin Dermatology Dermascope Light
Precio habitual
$49.99
Precio habitual
$99.99
Precio de oferta
$49.99
Precio unitario
/
por
Los gastos de envío se calculan en la pantalla de pago.
Share